To make good decisions, it is vital to know the current condition of the field. Core Project 1 develops novel ground and aerial vehicles that operate autonomously and provide precisely georeferenced, phenotypic data from single plant organs over the experimental plot to the field scale. We register 3D structural models of the same plant over time, leading to a 4D reconstruction. Our aim is to develop a new generation of mapping systems as well as a better understanding of the spatio-temporal dynamics of structural and functional plant traits. The goal is to reconstruct several hundred individual plants per day in an experimental field design.
Research Videos

Modern Sensing Applications for Analysing Plant Physiology and Interaction in Mixed Cropping
PhenoRob PhD Student Julie Kraemer talks about her research within Core Project 1 ” 4D Crop Reconstruction” and Core Project 5 “New Field Arrangements”.

Uwe Rascher: Measuring and understanding the dynamics of plant photosynthesis across scales…
Measuring and understanding the dynamics of plant photosynthesis across scales – from single plants to satellites Prof. Dr. Uwe Rascher is Principal Investigator at PhenoRob and Professor of Quantitative Physiology of Crops, Institute of Bio- and Geosciences (IBG-2), Forschungszentrum Jülich and Institute of Crop Science and Resource Conservation (INRES), University of Bonn Rascher et. al. (2015) Sun-induced fluorescence – a new probe of photosynthesis: First maps from the imaging spectrometer HyPlant Global Change Biology, 21, 4673-4684 https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13017 Siegmann et. al. (2019) The High-Performance Airborne Imaging Spectrometer HyPlant—From Raw Images to Top-of-Canopy Reflectance and Fluorescence Products: Introduction of an Automatized Processing Chain Remote Sensing, 11, article no. 2760 https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11232760
Sven Behnke, University of Bonn and Uwe Rascher, FZJ (11.03.2022)
Sven Behnke (University of Bonn) and Uwe Rascher (FZJ) give a talk on “In-Field 4D Crop Reconstruction: Measuring and modeling individual plants and canopies in 3D over time with mobile robots”

Lasse Klingbeil: Pheno4D: A spatio-temporal dataset of maize and tomato plant point clouds…
Dr. Lasse Klingbeil is Postdoc at the Institute of Geodesy and Geoinformation (IGG), University of Bonn and PhenoRob Member. Pheno4D: A spatio-temporal dataset of maize and tomato plant point clouds for phenotyping and advanced plant analysis D. Schunck, F. Magistri, R. A. Rosu, A. Cornelißen, N. Chebrolu, S. Paulus, J. Léon, S. Behnke, C. Stachniss, H. Kuhlmann, and L. Klingbeil PLOS ONE, vol. 16, iss. 8, pp. 1-18, 2021 Paper: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0256340 Data: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/data/pheno4d/

Shortcut Hulls: Vertex-restricted Outer Simplifications of Polygons by A. Bonerath et al.
This short paper trailer video is based on the following publication: A. Bonerath, J. Haunert, J. S. B. Mitchell, and B. Niedermann, “Shortcut Hulls: Vertex-restricted Outer Simplifications of Polygons,” in Proceedings of the 33rd Canadian Conference on Computational Geometry , 2021, pp. 12-23.

LatticeNet: fast spatio-temporal point cloud segmentation using permutohedral lattices (Rosu et al.)
This short paper trailer video is based on the following publication: R. A. Rosu, P. Schütt, J. Quenzel, and S. Behnke, “LatticeNet: fast spatio-temporal point cloud segmentation using permutohedral lattices,” Autonomous Robots, p. 1-16, 2021.
RAL-ICRA’22: Joint Plant and Leaf Instance Segmentation on Field-Scale UAV Imagery by Weyler et al.
J. Weyler, J. Quakernack, P. Lottes, J. Behley, and C. Stachniss, “Joint Plant and Leaf Instance Segmentation on Field-Scale UAV Imagery,” IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L), vol. 7, iss. 2, pp. 3787-3794, 2022. doi:10.1109/LRA.2022.3147462 PDF: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/weyler2022ral.pdf #UniBonn #StachnissLab #robotics

WACV’22: In-Field Phenotyping Based on Crop Leaf and Plant Instance Segmentation by Weyler et al.
J. Weyler, F. and Magistri, P. Seitz, J. Behley, and C. Stachniss, “In-Field Phenotyping Based on Crop Leaf and Plant Instance Segmentation,” in Proc. of the Winter Conf. on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), 2022. PDF: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/weyler2022wacv.pdf #UniBonn #StachnissLab #robotics

ICRA’21: Phenotyping Exploiting Differentiable Rendering with Consistency Loss by Magistri et al.
F. Magistri, N. Chebrolu, J. Behley, and C. Stachniss, “Towards In-Field Phenotyping Exploiting Differentiable Rendering with Self-Consistency Loss,” in Proceedings of the IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics & Automation (ICRA), 2021. Paper: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/magistri2021icra.pdf #UniBonn #StachnissLab #robotics #PhenoRob #neuralnetworks #talk
Talk by X. Chen: Range Image-based LiDAR Localization for Autonomous Vehicles (ICRA’21)
X. Chen, I. Vizzo, T. Läbe, J. Behley, and C. Stachniss, “Range Image-based LiDAR Localization for Autonomous Vehicles,” in Proceedings of the IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics & Automation (ICRA), 2021. Paper: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/chen2021icra.pdf Code: https://github.com/PRBonn/range-mcl #UniBonn #StachnissLab #robotics #autonomouscars #neuralnetworks #talk

Talk by J. Quenzel on Beyond Photometric Consistency: Gradient-based Dissimilarity for VO (ICRA’20)
ICRA 2020 talk about the paper: J. Quenzel, R. A. Rosu, T. Laebe, C. Stachniss, and S. Behnke, “Beyond Photometric Consistency: Gradient-based Dissimilarity for Improving Visual Odometry and Stereo Matching,” in Proceedings of the IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics & Automation (ICRA), 2020. PDF: http://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/pdfs/quenzel2020icra.pdf

IROS’20: Segmentation-Based 4D Registration of Plants Point Clouds for Phenotyping by Magistri et al
F. Magistri, N. Chebrolu, and C. Stachniss, “Segmentation-Based 4D Registration of Plants Point Clouds ,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2020. Paper: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/magistri2020iros.pdf #UniBonn #StachnissLab #robotics #PhenoRob #talk
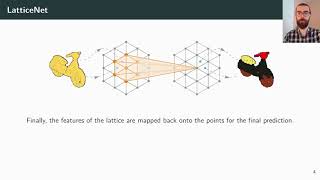
RSS 2020′: LatticeNet: Fast Point Cloud Segmentation Using Permutohedral Lattices
LatticeNet: Fast Point Cloud Segmentation Using Permutohedral Lattices by Radu Alexandru Rosu, Peer Schütt, Jan Quenzel, Sven Behnke Deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have shown outstanding performance in the task of semantically segmenting images. However, applying the same methods on 3D data still poses challenges due to the heavy memory requirements and the lack of structured data. Here, we propose LatticeNet, a novel approach for 3D semantic segmentation, which takes as input raw point clouds. A PointNet describes the local geometry which we embed into a sparse permutohedral lattice. The lattice allows for fast convolutions while keeping a low memory footprint. Further, we introduce DeformSlice, a novel learned data-dependent interpolation for projecting lattice features back onto the point cloud. We present results of 3D segmentation on various datasets where our method achieves state-of-the-art performance.
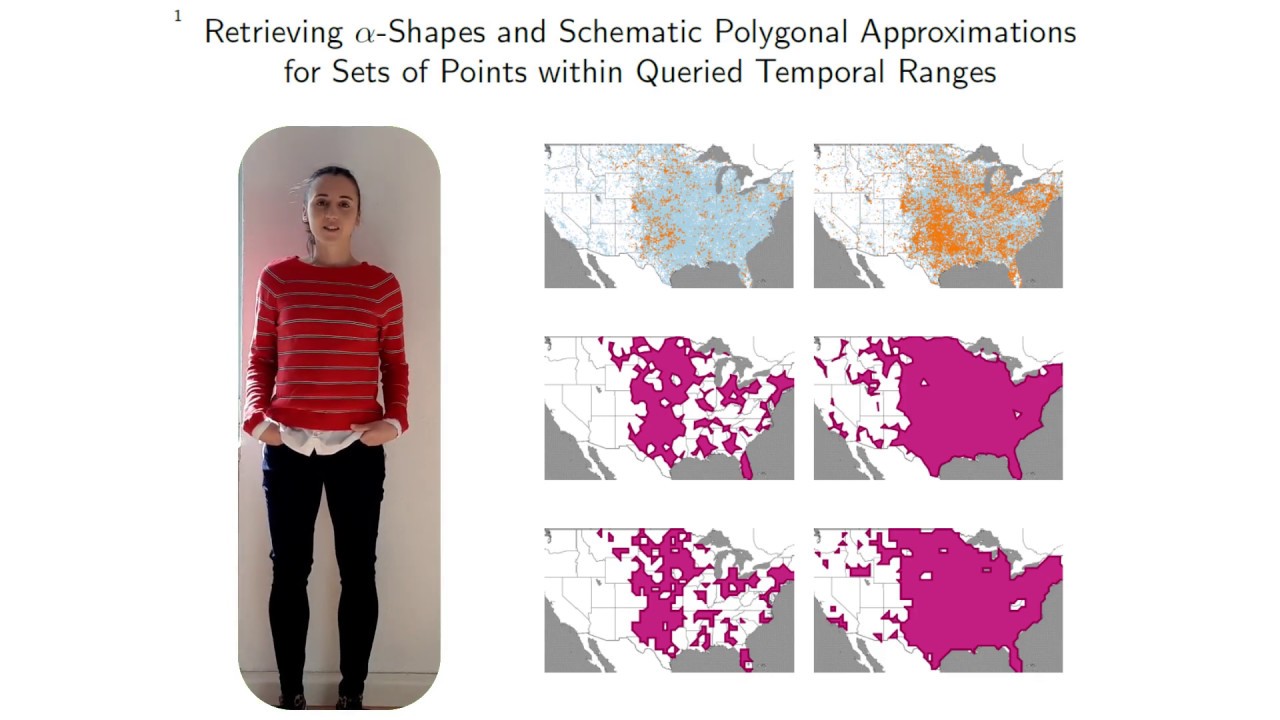
SIGSPATIAL’2019: Retrieving alpha-Shapes and Schematic Polygonal Approximations for Sets of Points..
Retrieving alpha-Shapes and Schematic Polygonal Approximations for Sets of Points within Queried Temporal Ranges by A. Bonerath, B. Niedermann und J.-H. Haunert In Proceedings of the 27th ACM SIGSPATIAL International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, 2019
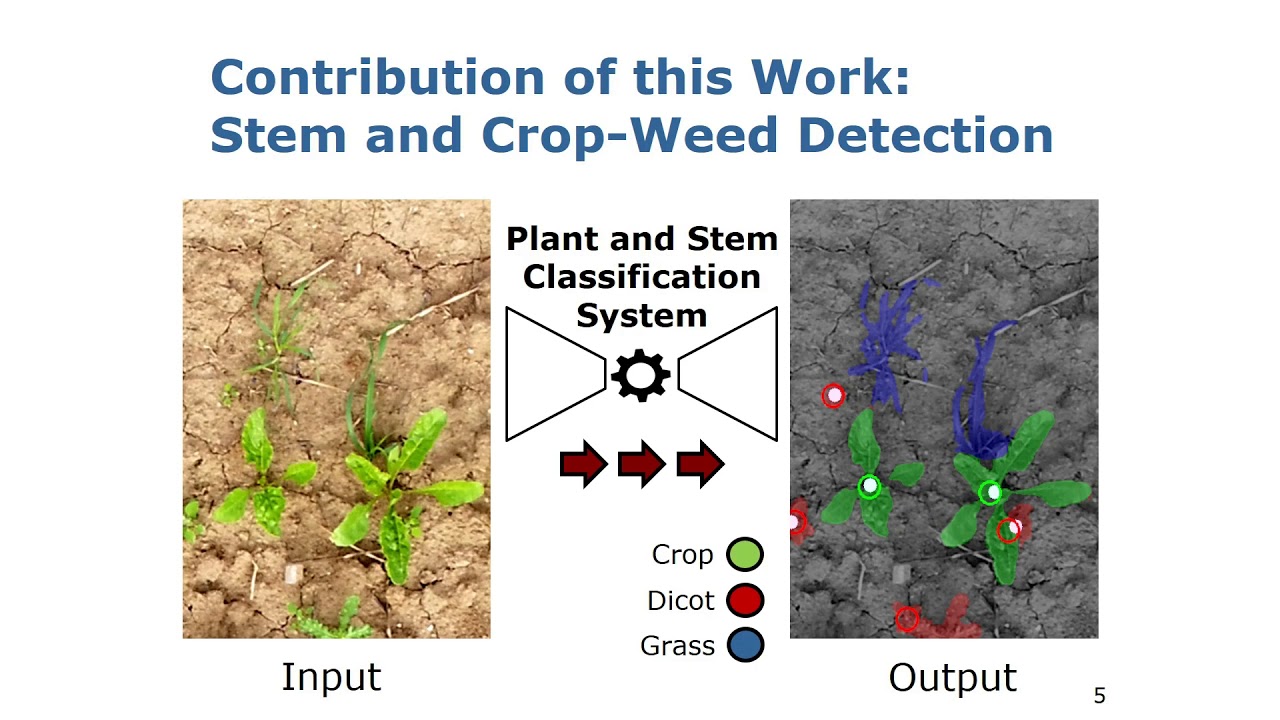
IROS’18: Joint Stem Detection and Crop-Weed Classification for Plant-specific Treatment
Trailer for the paper: Joint Stem Detection and Crop-Weed Classification for Plant-specific Treatment in Precision Farming by P. Lottes, J. Behley, N. Chebrolu, A. Milioto, and C. Stachniss, IROS 2018.

RAL’18: FCNs with Sequential Information for Robust Crop and Weed Detection by Lottes et al.
Trailer for the paper: Fully Convolutional Networks with Sequential Information for Robust Crop and Weed Detection in Precision Farming by P. Lottes, J. Behley, A. Milioto, and C. Stachniss, RAL 2018

RAL-ICRA’19: Effective Visual Place Recognition Using Multi-Sequence Maps by Vysotska & Stachniss
O. Vysotska and C. Stachniss, “Effective Visual Place Recognition Using Multi-Sequence Maps,” IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L) and presentation at ICRA, 2019. PDF: http://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/vysotska2019ral.pdf
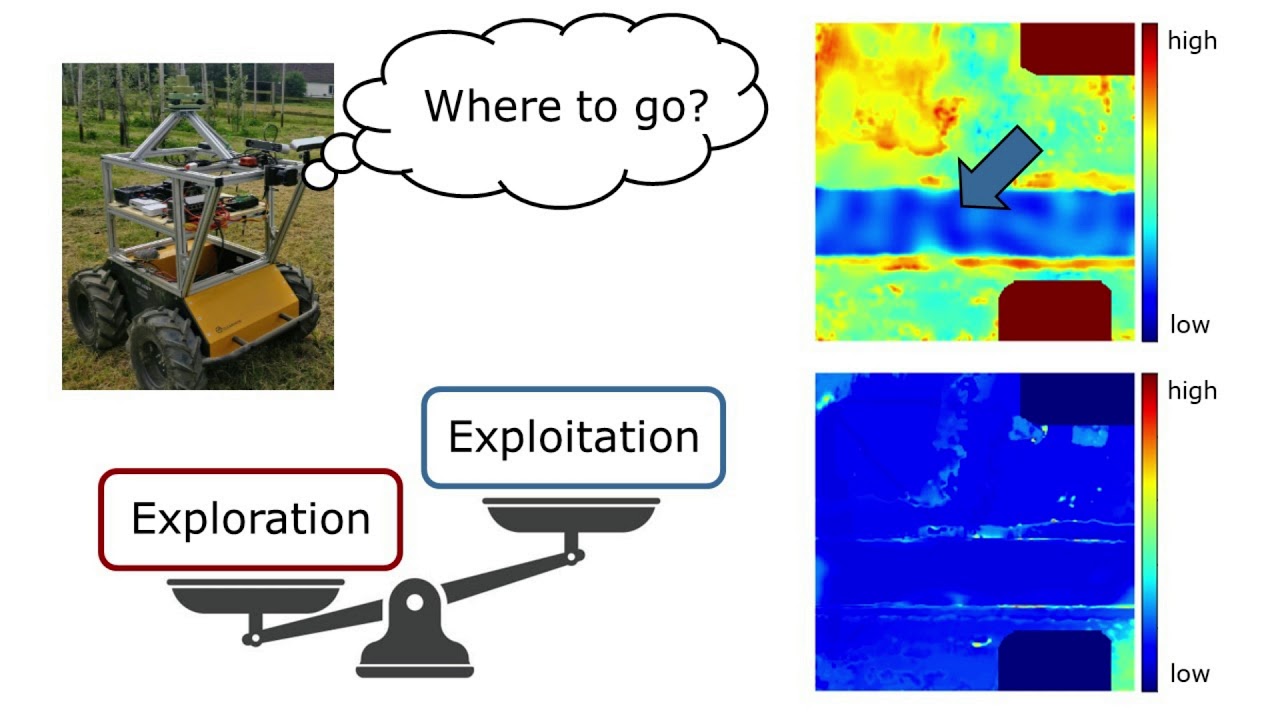
ICRA’19: Actively Improving Robot Navigation On Different Terrains Using GPMMs by Nardi et al.
L. Nardi and C. Stachniss, “Actively Improving Robot Navigation On Different Terrains Using Gaussian Process Mixture Models,” in Proc. of the IEEE Intl. Conf. on Robotics & Automation (ICRA) , 2019. http://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/nardi2019icra-airn.pdf
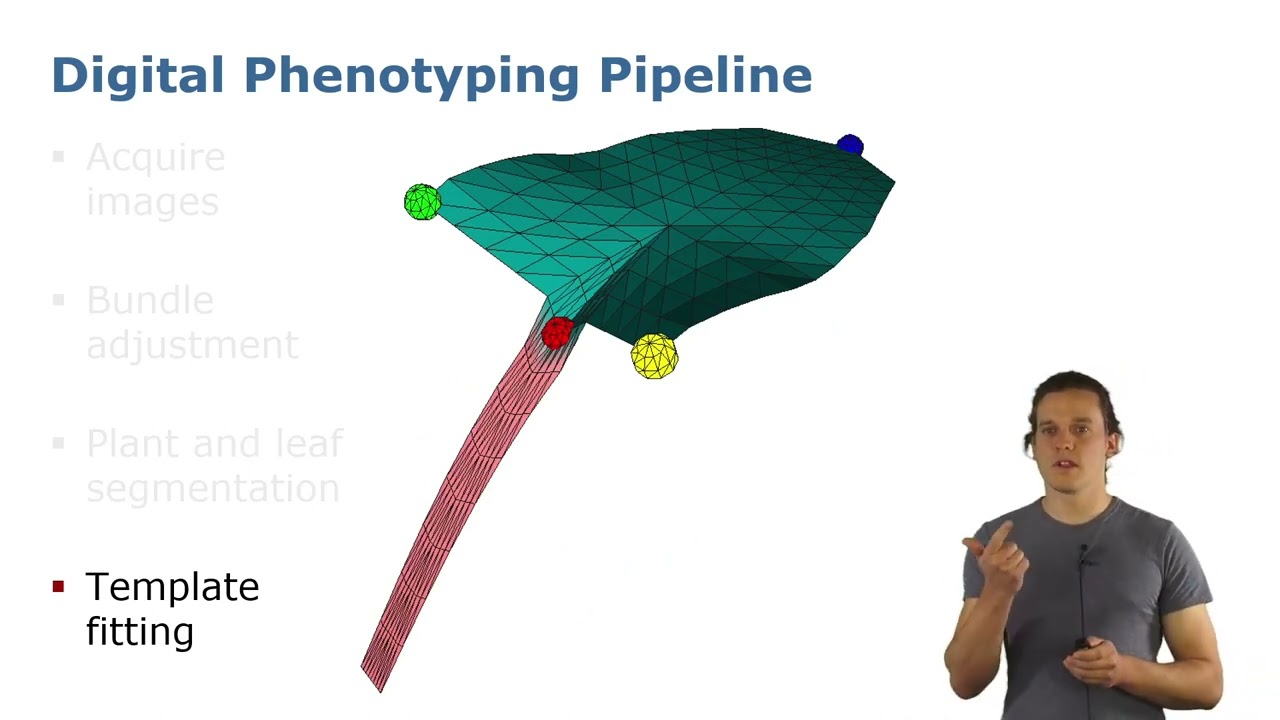
ICRA’22: Precise 3D Reconstruction of Plants from UAV Imagery … by Marks et al.
E. Marks, F. Magistri, and C. Stachniss, “Precise 3D Reconstruction of Plants from UAV Imagery Combining Bundle Adjustment and Template Matching,” in Proc.~of the IEEE Intl.~Conf.~on Robotics & Automation (ICRA), 2022. PDF: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/marks2022icra.pdf #UniBonn #StachnissLab #robotics

Faces of PhenoRob: Christian Lenz
In Faces of PhenoRob, we introduce you to some of PhenoRob’s many members: from senior faculty to PhDs, this is your chance to meet them all and learn more about the work they do! In this video, you’ll meet Christian Lenz, PhenoRob PhD Student.

Hierarchical Approach for Joint Semantic, Plant & Leaf Instance Segmentation in the Agricult. Domain
This short trailer is based on the following publication: G. Roggiolani, M. Sodano, F. Magistri, T. Guadagnino, J. Behley, and C. Stachniss, “Hierarchical Approach for Joint Semantic, Plant Instance, and Leaf Instance Segmentation in the Agricultural Domain,” in Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics & Automation (ICRA), 2023.

On Domain-Specific Pre-Training for Effective Semantic Perception in Agricult. Robotics (Roggiolani)
This short trailer is based on the following publication: G. Roggiolani, F. Magistri, T. Guadagnino, G. Grisetti, C. Stachniss, and J. Behley, “On Domain-Specific Pre-Training for Effective Semantic Perception in Agricultural Robotics,” Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics & Automation (ICRA), 2023.
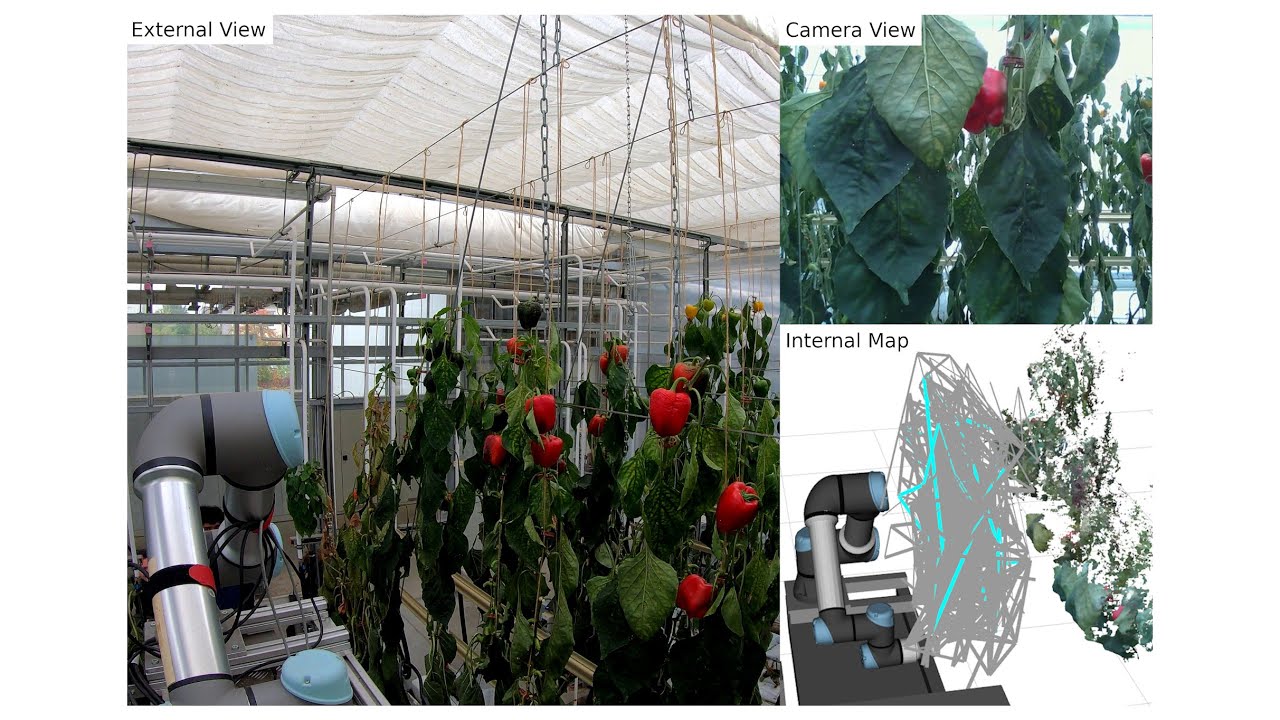
Graph-based View Motion Planning for Fruit Detection
This video demonstrates the work presented in our paper “Graph-based View Motion Planning for Fruit Detection” by T. Zaenker, J. Rückin, R. Menon, M. Popović, and M. Bennewitz, submitted to the International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2023. Paper link: https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.03048 The view motion planner generates view pose candidates from targets to find new and cover partially detected fruits and connects them to create a graph of efficiently reachable and information-rich poses. That graph is searched to obtain the path with the highest estimated information gain and updated with the collected observations to adaptively target new fruit clusters. Therefore, it can explore segments in a structured way to optimize fruit coverage with a limited time budget. The video shows the planner applied in a commercial glasshouse environment and in a simulation designed to mimic our real-world setup, which we used to evaluate the performance. Code: https://github.com/Eruvae/view_motion_planner
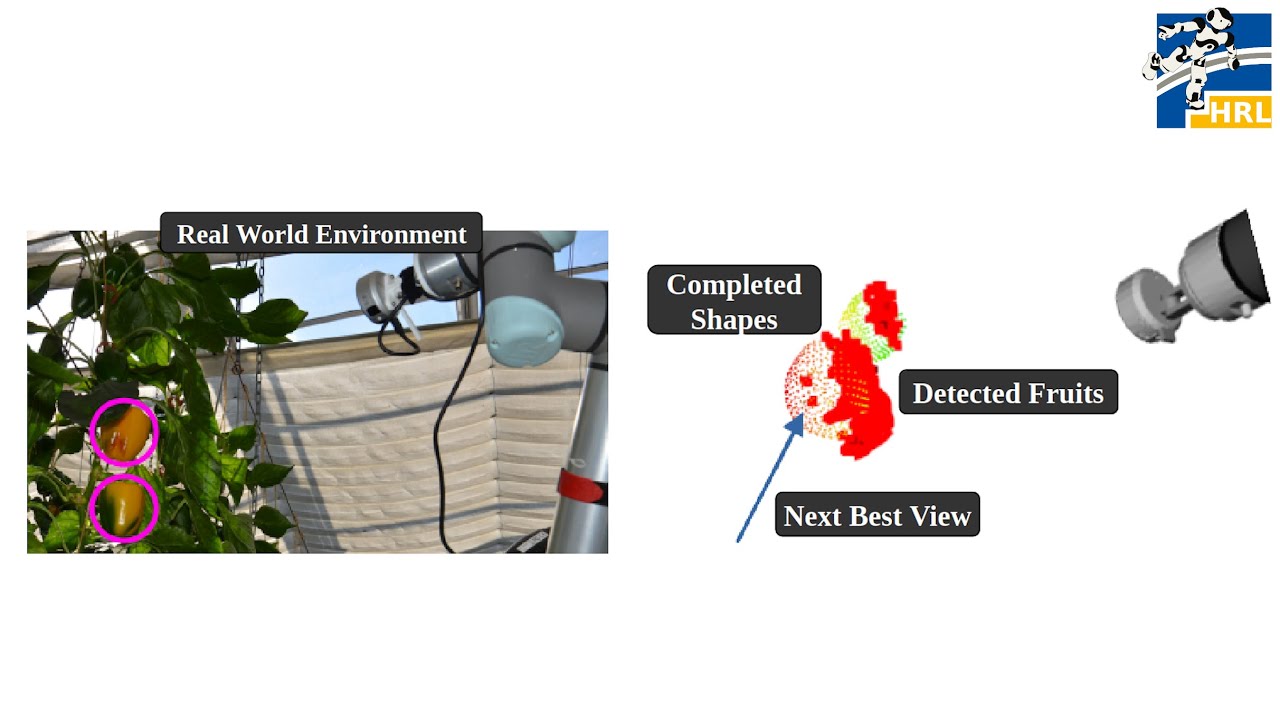
NBV-SC: Next Best View Planning based on Shape Completion for Fruit Mapping and Reconstruction
This video demonstrates the work presented in our paper “NBV-SC: Next Best View Planning based on Shape Completion for Fruit Mapping and Reconstruction” by R. Menon, T. Zaenker, N. Dengler and M. Bennewitz, submitted to the International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2023. State-of-the-art viewpoint planning approaches utilize computationally expensive ray casting operations to find the next best viewpoint. In our paper, we present a novel viewpoint planning approach that explicitly uses information about the predicted fruit shapes to compute targeted viewpoints that observe as yet unobserved parts of the fruits. Furthermore, we formulate the concept of viewpoint dissimilarity to reduce the sampling space for more efficient selection of useful, dissimilar viewpoints. In comparative experiments with a state-of-the-art viewpoint planner, we demonstrate improvement not only in the estimation of the fruit sizes, but also in their reconstruction, while significantly reducing the planning time. Finally, we show the viability of our approach for mapping sweet peppers plants with a real robotic system in a commercial glasshouse. Paper link https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.15376

Viewpoint Push Planning for Mapping of Unknown Confined Spaces
This video demonstrates the work presented in our paper “Viewpoint Push Planning for Mapping of Unknown Confined Spaces” by N. Dengler, S. Pan, V. Kalagaturu, R. Menon, M. Dawood and Maren Bennewitz, submitted to the International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2023. Paper link: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2303.03126.pdf The mapping of confined spaces such as shelves is an especially challenging task in the domain of viewpoint planning, since objects occlude each other and the scene can only be observed from the front, thus with limited possible viewpoints. In this video, we show our deep reinforcement learning framework that generates promising views aiming at reducing the map entropy. Additionally, the pipeline extends standard viewpoint planning by predicting adequate minimally invasive push actions to uncover occluded objects and increase the visible space. Using a 2.5D occupancy height map as state representation that can be efficiently updated, our system decides whether to plan a new viewpoint or perform a push. As the real-world experimental results with a robotic arm show, our system is able to significantly increase the mapped space compared to different baselines, while the executed push actions highly benefit the viewpoint planner with only minor changes to the object configuration. Code: https://github.com/NilsDengler/view-point-pushing

PhenoRob PhD Graduate Talks: Laura Zabawa
Laura Zabawa gives a talk on “Contributions to image-based high-throughput phenotyping in viticulture” after successfully completing her PhD as part of a PhenoRob partner project. In the PhenoRob PhD Graduate Talks, recent PhenoRob graduates share about their research within the Cluster of Excellence.

PermutoSDF: Fast Multi-View Reconstruction with Implicit Surfaces using Permutohedral Lattices
Neural radiance-density field methods have become increasingly popular for the task of novel-view rendering. Their recent extension to hash-based positional encoding ensures fast training and inference with visually pleasing results. However, density-based methods struggle with recovering accurate surface geometry. Hybrid methods alleviate this issue by optimizing the density based on an underlying SDF. However, current SDF methods are overly smooth and miss fine geometric details. In this work, we combine the strengths of these two lines of work in a novel hash-based implicit surface representation. We propose improvements to the two areas by replacing the voxel hash encoding with a permutohedral lattice which optimizes faster, especially for higher dimensions. We additionally propose a regularization scheme which is crucial for recovering high-frequency geometric detail. We evaluate our method on multiple datasets and show that we can recover geometric detail at the level of pores and wrinkles while using only RGB images for supervision. Furthermore, using sphere tracing we can render novel views at 30 fps on an RTX 3090. The paper, animations, and code is available at https://radualexandru.github.io/permuto_sdf

DawnIK: Decentralized Collision-Aware Inverse Kinematics Solver for Heterogeneous Multi-Arm Systems
This video demonstrates the work presented in our paper “DawnIK: Decentralized Collision-Aware Inverse Kinematics Solver for Heterogeneous Multi-Arm Systems” by S. Marangoz, R. Menon, N. Dengler, and M. Bennewitz, submitted to IEEE-RAS International Conference on Humanoid Robots (Humanoids), 2023. With collaborative service robots gaining traction, different robotic systems have to work in close proximity. This means that the current inverse kinematics approaches do not have only to avoid collisions with themselves but also collisions with other robot arms. Therefore, we present a novel approach to compute inverse kinematics for serial manipulators that take into account different constraints while trying to reach a desired end-effector pose that avoids collisions with themselves and other arms. We formulate different constraints as weighted cost functions to be optimized by a non-linear optimization solver. Our approach is superior to a state-of-the-art inverse kinematics solver in terms of collision avoidance in the presence of multiple arms in confined spaces with no collisions occurring in all the experimental scenarios. When the probability of collision is low, our approach shows better performance at trajectory tracking as well. Additionally, our approach is capable of simultaneous yet decentralized control of multiple arms for trajectory tracking in intersecting workspace without any collisions. Paper link https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.12750

Image-Coupled Volume Propagation for Stereo Matching by Oh-Hun Kwon and Eduard Zell
This trailer video is based on following publication: O. Kwon and E. Zell, “Image-Coupled Volume Propagation for Stereo Matching,” in 2023 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), 2023, pp. 2510-2514. doi:10.1109/ICIP49359.2023.10222247

Spatial Optimization via Mathematical Programming: Fundamentals and Applications
Jan-Henrik Haunert, Professor and head of the Geoinformation Group, Institute of Geodesy and Geoinformation (IGG) at the University of Bonn, gives a PhenoRob Interdisciplinary Lecture [PILS] on “Spatial Optimization via Mathematical Programming: Fundamentals and Applications in Harvest Scheduling, Districting, and Visualizing Trade Agreements”.

An overview of plant representations in 3D and its implications
Eduard Zell, who is currently leading a new research group at the PhenoRob Cluster of Excellence (University of Bonn), that focuses on the acquisition and post-processing of 4D data, mainly plants and soon again humans, gives a PhenoRob Interdisciplinary lecture [PILS] on the topic of “An overview of plant representations in 3D and its implications”.
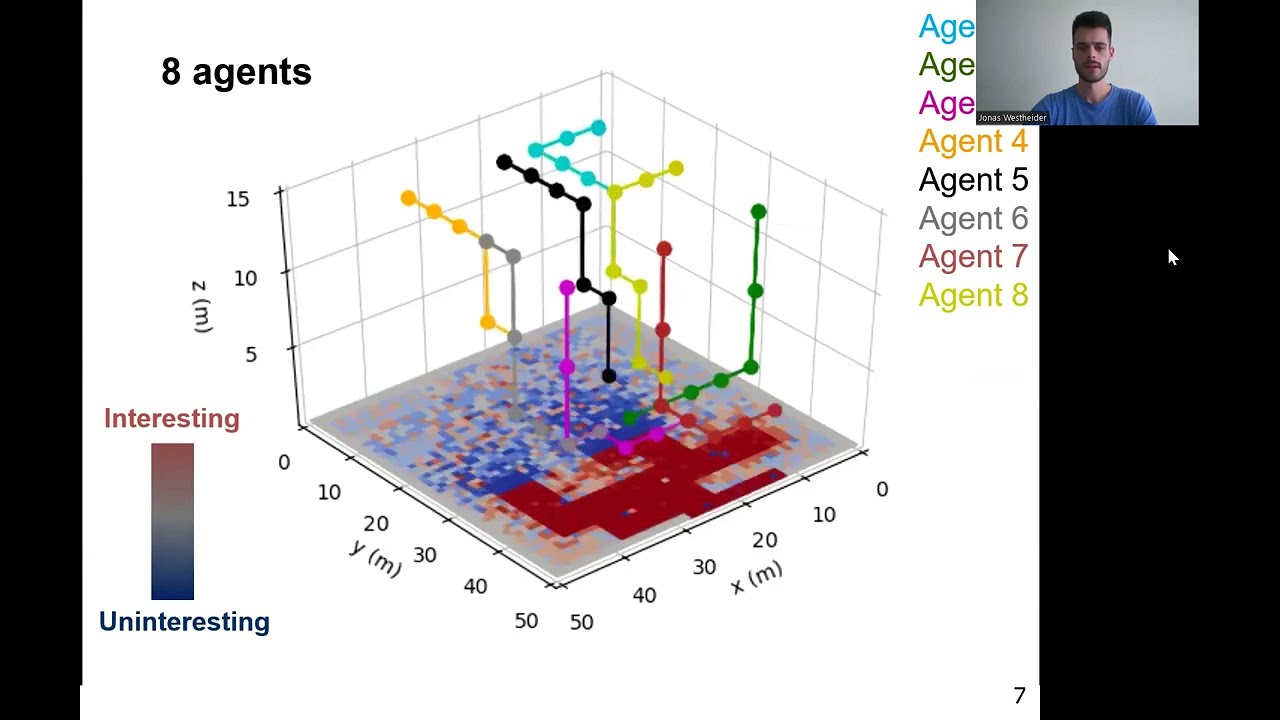
Multi-UAV Adaptive Path Planning Using Deep Reinforcement Learning
Jonas Westheider is a PhD Student at the Institute of Geodesy and Geoinformation (IGG), University of Bonn. Westheider, J., Rückin, J., & Popović, M., “Multi-UAV Adaptive Path Planning Using Deep Reinforcement Learning”. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.01150. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.robot.2022.104288

Physically modelled scaling and ML retrievals of plant traits from remotely sensed spectral observ.
Zbyněk Malenovský presents in this PhenoRob Interdisciplinary Lecture Series [PILS] “Physically modelled scaling and machine-learning retrievals of plant functional traits from remotely sensed spectral observations” He is an optical remote sensing and plant eco-physiology scientist based at the University of Bonn.

Faces of PhenoRob: Annika Bonerath
In Faces of PhenoRob, we introduce you to some of PhenoRob’s many members: from senior faculty to PhDs, this is your chance to meet them all and learn more about the work they do! In this video, you’ll meet Annika Bonerath, PhenoRob PhD Student and Research Data Manager in the PhenoRob Cluster Office.

ICRA 2020 Presentation – Visual-Servoing based Navigation for Monitoring Row-Crop Fields
In this project, we propose a framework tailored for navigation in row-crop fields by exploiting the regular crop-row structure present in the fields. Our approach uses only the images from on-board cameras without the need for performing explicit localization or maintaining a map of the field. It allows the robot to follow the crop-rows accurately and handles the switch to the next row seamlessly within the same framework. We implemented our approach using C ++ and ROS and thoroughly tested it in several simulated environments with different shapes and sizes of field Code on Github: https://github.com/PRBonn/visual-crop-row-navigation

IROS’19: ReFusion: 3D Reconstruction in Dynamic Environments for RGB-D Cameras… by Palazzolo et al
ReFusion: 3D Reconstruction in Dynamic Environments for RGB-D Cameras Exploiting Residuals by Emanuele Palazzolo, Jens Behley, Philipp Lottes, Philippe Giguere, and Cyrill Stachniss IROS 2019 Arxiv paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.02082 Code release: https://github.com/PRBonn/refusion

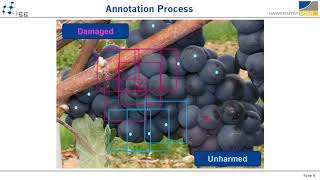
Laura Zabawa – Counting grapevine berries in images via semantic segmentation
International Conference on Digital Technologies for Sustainable Crop Production (DIGICROP 2020) • November 1-10, 2020 • http://digicrop.de/
Laura Zabawa – Counting grapevine berries in images via semantic segmentation (Trailer)
Watch the full presentation: http://digicrop.de/program/counting-grapevine-berries-in-images-via-semantic-segmentation/
IROS’20: Learning an Overlap-based Observation Model for 3D LiDAR Localization by Chen et al.
Trailer Video for the work: X. Chen, T. Läbe, L. Nardi, J. Behley, and C. Stachniss, “Learning an Overlap-based Observation Model for 3D LiDAR Localization,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2020. Paper: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/chen2020iros.pdf Code available!

Talk by X. Chen on Learning an Overlap-based Observation Model for 3D LiDAR Localization (IROS’20)
X. Chen, T. Läbe, L. Nardi, J. Behley, and C. Stachniss, “Learning an Overlap-based Observation Model for 3D LiDAR Localization,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2020. PAPER: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/chen2020iros.pdf CODE: https://github.com/PRBonn/overlap_localization
Talk by F. Magistri: Segmentation-Based 4D Registration of Plants Point Clouds (IROS’20)
Paper: F. Magistri, N. Chebrolu, and C. Stachniss, “Segmentation-Based 4D Registration of Plants Point Clouds for Phenotyping,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2020. PDF: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/magistri2020iros.pdf

Hypermap Mapping Framework and its Application to Autonomous Semantic Exploration by T Zaenker et al
This paper trailer video is based on the following publication: T. Zaenker, F. Verdoja, and V. Kyrki, “Hypermap Mapping Framework and its Application to Autonomous Semantic Exploration,” in 2020 IEEE Conference on Multisensor Fusion and Integration, 2020. To learn more, check out the full publication here: https://acris.aalto.fi/ws/portalfiles/portal/53865812/ELEC_Zaenker_etal_Hypermap_Mapping_Framework_MFI2020_acceptedauthormanuscript.pdf
IROS’20: LiDAR Panoptic Segmentation for Autonomous Driving presented by J. Behley
Trailer video for the paper: A. Milioto, J. Behley, C. McCool, and C. Stachniss, “LiDAR Panoptic Segmentation for Autonomous Driving,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ Int. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2020. Paper: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/milioto2020iros.pdf

Talk by X. Chen on OverlapNet – Loop Closing for LiDAR-based SLAM (RSS’20)
Talk for the RSS 2020 paper: X. Chen, T. Läbe, A. Milioto, T. Röhling, O. Vysotska, A. Haag, J. Behley, and C. Stachniss, “OverlapNet: Loop Closing for LiDAR-based SLAM,” in Proceedings of Robotics: Science and Systems (RSS), 2020. Paper: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/chen2020rss.pdf Code available: https://github.com/PRBonn/OverlapNet

RSS’20: OverlapNet – Loop Closing for LiDAR-based SLAM by Chen et al.
X. Chen, T. Läbe, A. Milioto, T. Röhling, O. Vysotska, A. Haag, J. Behley, and C. Stachniss, “OverlapNet: Loop Closing for LiDAR-based SLAM,” in Proceedings of Robotics: Science and Systems (RSS), 2020. Paper: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/chen2020rss.pdf Code: https://github.com/PRBonn/OverlapNet (to be released before RSS) Vide: https://youtu.be/YTfliBco6aw

Talk by N. Chebrolu on Spatio-Temporal Non-Rigid Registration of 3D Point Clouds of Plants (ICRA’20)
ICRA 2020 talk about the paper: N. Chebrolu, T. Laebe, and C. Stachniss, “Spatio-Temporal Non-Rigid Registration of 3D Point Clouds of Plants,” in Proceedings of the IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics & Automation (ICRA), 2020. https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/chebrolu2020icra.pdf

Zoomless Maps: External Labeling Methods for the Interactive Exploration of Dense Point Sets at a F
Authors: Sven Gedicke, Annika Bonerath, Benjamin Niedermann, Jan-Henrik Haunert VIS website: http://ieeevis.org/year/2020/welcome Visualizing spatial data on small-screen devices such as smartphones and smartwatches poses new challenges in computational cartography. The current interfaces for map exploration require their users to zoom in and out frequently. Indeed, zooming and panning are tools suitable for choosing the map extent corresponding to an area of interest. They are not as suitable, however, for resolving the graphical clutter caused by a high feature density since zooming in to a large map scale leads to a loss of context. Therefore, in this paper, we present new external labeling methods that allow a user to navigate through dense sets of points of interest while keeping the current map extent fixed. We provide a unified model, in which labels are placed at the boundary of the map and visually associated with the corresponding features via connecting lines, which are called leaders. Since the screen space is limited, labeling all features at the same time is impractical. Therefore, at any time, we label a subset of the features. We offer interaction techniques to change the current selection of features systematically and, thus, give the user access to all features. We distinguish three methods, which allow the user either to slide the labels along the bottom side of the map or to browse the labels based on pages or stacks. We present a generic algorithmic framework that provides us with the possibility of expressing the different variants of interaction techniques as optimization problems in a unified way. We propose both exact algorithms and fast and simple heuristics that solve the optimization problems taking into account different criteria such as the ranking of the labels, the total leader length as well as the distance between leaders. In experiments on real-world data we evaluate these algorithms and discuss the three variants with respect to their strengths and weaknesses proving the flexibility of the presented algorithmic framework.

ICRA’21: Range Image-based LiDAR Localization for Autonomous Vehicles by Chen et al.
X. Chen, I. Vizzo, T. Läbe, J. Behley, and C. Stachniss, “Range Image-based LiDAR Localization for Autonomous Vehicles,” in Proceedings of the IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics & Automation (ICRA), 2021. https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/chen2021icra.pdf #UniBonn #StachnissLab #robotics #autonomouscars #talk
Talk by I. Vizzo: Poisson Surface Reconstruction for LiDAR Odometry and Mapping (ICRA’21)
I. Vizzo, X. Chen, N. Chebrolu, J. Behley, and C. Stachniss, “Poisson Surface Reconstruction for LiDAR Odometry and Mapping,” in Proceedings of the IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics & Automation (ICRA), 2021. Paper: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/vizzo2021icra.pdf Code: https://github.com/PRBonn/puma #UniBonn #StachnissLab #robotics #autonomouscars #slam #talk

Talk by F. Magistri: Phenotyping Exploiting Differentiable Rendering with Self-Consistency (ICRA’21)
F. Magistri, N. Chebrolu, J. Behley, and C. Stachniss, “Towards In-Field Phenotyping Exploiting Differentiable Rendering with Self-Consistency Loss,” in Proceedings of the IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics & Automation (ICRA), 2021. Paper: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/magistri2021icra.pdf #UniBonn #StachnissLab #robotics #PhenoRob #neuralnetworks #talk
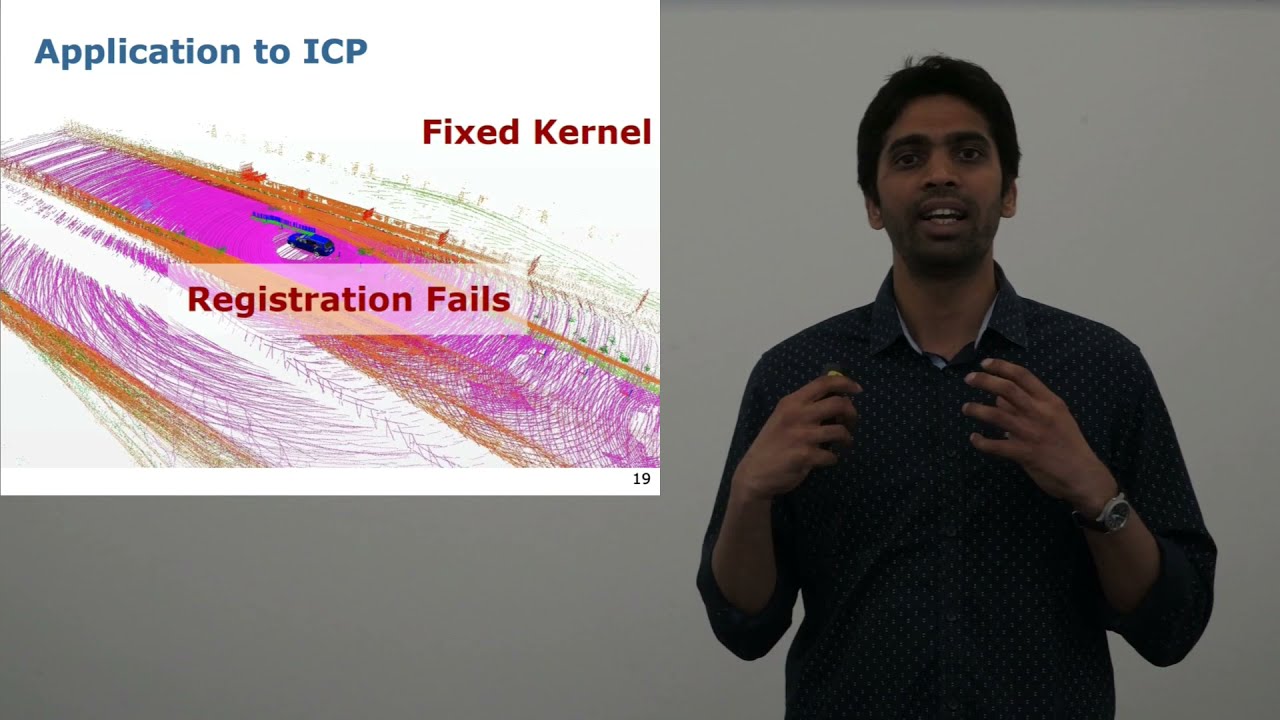
Talk by N. Chebrolu: Adaptive Robust Kernels for Non-Linear Least Squares Problems (RAL+ICRA’21)
N. Chebrolu, T. Läbe, O. Vysotska, J. Behley, and C. Stachniss, “Adaptive Robust Kernels for Non-Linear Least Squares Problems,” IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L), vol. 6, pp. 2240-2247, 2021. doi:10.1109/LRA.2021.3061331 https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/chebrolu2021ral.pdf #UniBonn #StachnissLab #robotics #autonomouscars #slam #talk
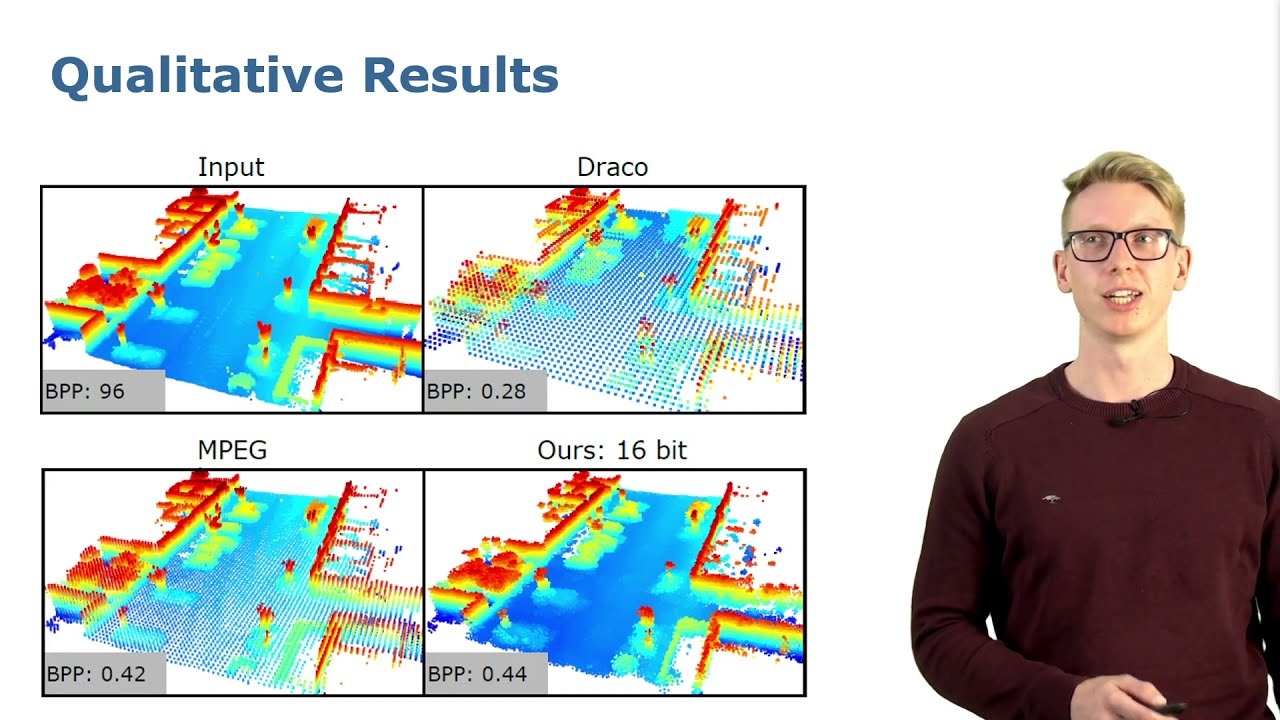
Talk by L. Wiesmann: Deep Compression for Dense Point Cloud Maps (RAL-ICRA 2021)
L. Wiesmann, A. Milioto, X. Chen, C. Stachniss, and J. Behley, “Deep Compression for Dense Point Cloud Maps,” IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L), vol. 6, pp. 2060-2067, 2021. doi:10.1109/LRA.2021.3059633 Code: https://github.com/PRBonn/deep-point-map-compression Paper: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/wiesmann2021ral.pdf #UniBonn #StachnissLab #robotics #autonomouscars #neuralnetworks #talk

Nived Chebrolu – Spatio-temporal registration of plant point clouds for phenotyping (Talk)
International Conference on Digital Technologies for Sustainable Crop Production (DIGICROP 2020) • November 1-10, 2020 • http://digicrop.de/

Nived Chebrolu – Spatio-temporal registration of plant point clouds for phenotyping (Trailer)
Watch the full presentation: http://digicrop.de/program/spatio-temporal-registration-of-plant-point-clouds-for-phenotyping/

Online Object-Oriented Semantic Mapping with the Toyota HSR Robot
This video demonstrates our semantic mapping framework, which is capable of online mapping and object updating given object detections from RGB-D data and provides various 2D and 3D representations of the mapped objects. Our mapping system is highly efficient and achieves a run time of more than 10 Hz. This paper describes our framework in detail: https://arxiv.org/abs/2011.06895
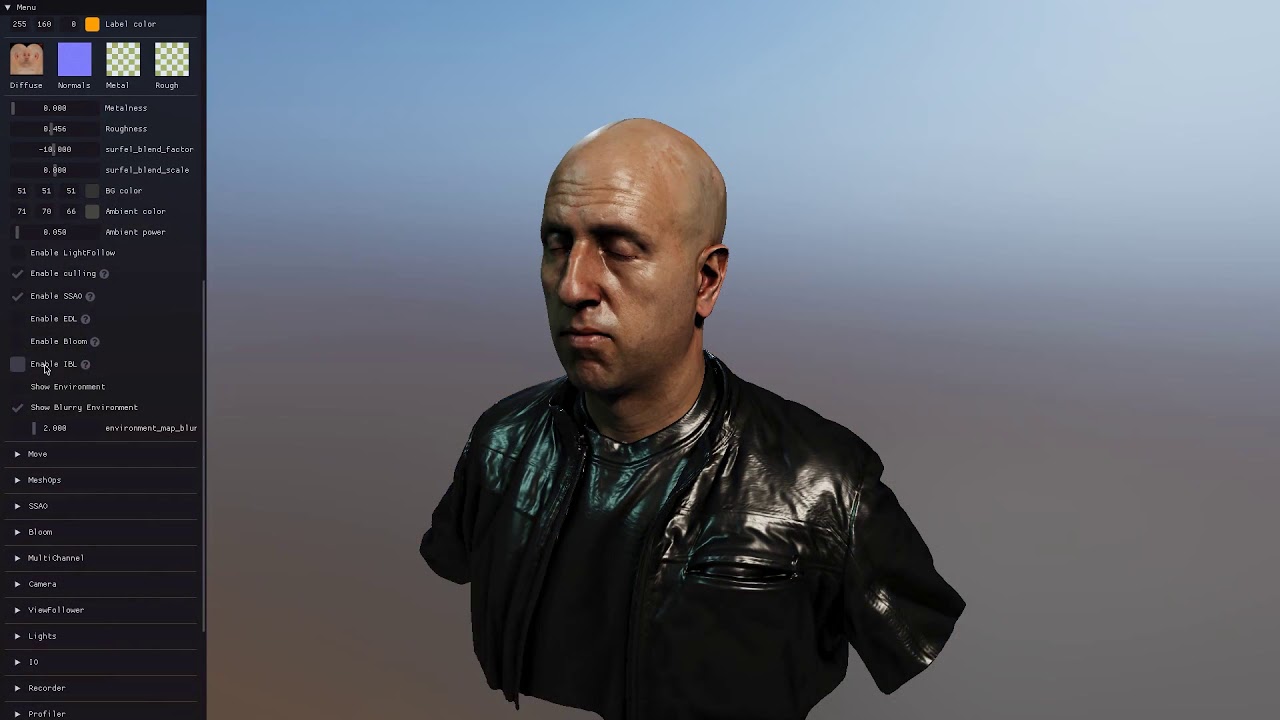

EasyPBR: A Lightweight Physically-Based Renderer
Presentation for paper by Radu Alexandru Rosu and Sven Behnke: “EasyPBR: A Lightweight Physically-Based Renderer” 16th International Conference on Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (GRAPP), 2021 Modern rendering libraries provide unprecedented realism, producing real-time photorealistic 3D graphics on commodity hardware. Visual fidelity, however, comes at the cost of increased complexity and difficulty of usage, with many rendering parameters requiring a deep understanding of the pipeline. We propose EasyPBR as an alternative rendering library that strikes a balance between ease-of-use and visual quality. EasyPBR consists of a deferred renderer that implements recent state-of-the-art approaches in physically based rendering. It offers an easy-to-use Python and C++ interface that allows high-quality images to be created in only a few lines of code or directly through a graphical user interface. The user can choose between fully controlling the rendering pipeline or letting EasyPBR automatically infer the best parameters based on the current scene composition. The EasyPBR library can help the community to more easily leverage the power of current GPUs to create realistic images. These can then be used as synthetic data for deep learning or for creating animations for academic purposes. http://www.ais.uni-bonn.de/papers/GRAPP_2021_Rosu_EasyPBR.pdf
RAL-ICRA’22: Contrastive Instance Association for 4D Panoptic Segmentation… by Marcuzzi et al.
R. Marcuzzi, L. Nunes, L. Wiesmann, I. Vizzo, J. Behley, and C. Stachniss, “Contrastive Instance Association for 4D Panoptic Segmentation using Sequences of 3D LiDAR Scans,” IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L), vol. 7, iss. 2, pp. 1550-1557, 2022. doi:10.1109/LRA.2022.3140439 PDF: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/marcuzzi2022ral.pdf #UniBonn #StachnissLab #robotics
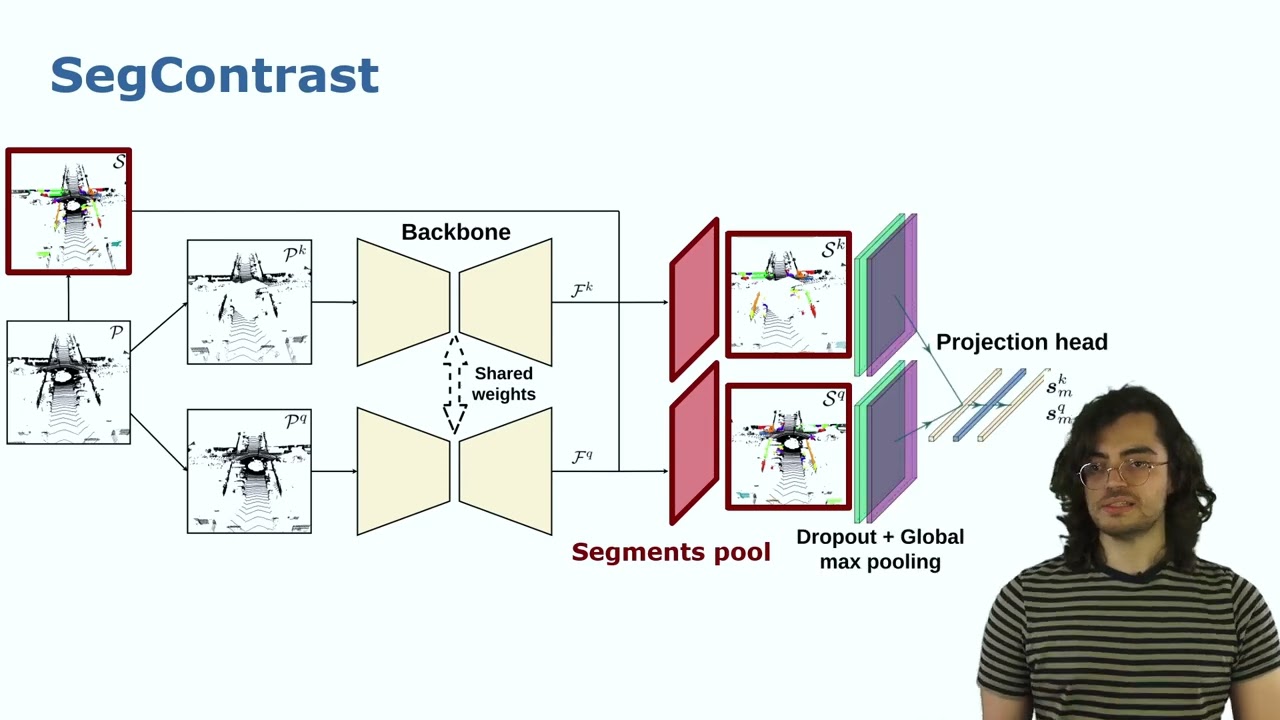
RAL-ICRA’22: SegContrast: 3D Point Cloud Feature Representation Learning … by Nunes et al.
L. Nunes, R. Marcuzzi, X. Chen, J. Behley, and C. Stachniss, “SegContrast: 3D Point Cloud Feature Representation Learning through Self-supervised Segment Discrimination,” IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L), vol. 7, iss. 2, pp. 2116-2123, 2022. doi:10.1109/LRA.2022.3142440 PDF: http://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/pdfs/nunes2022ral-icra.pdf CODE: https://github.com/PRBonn/segcontrast #UniBonn #StachnissLab #robotics

ICRA’22: Retriever: Point Cloud Retrieval in Compressed 3D Maps by Wiesmann et al.
L. Wiesmann, R. Marcuzzi, C. Stachniss, and J. Behley, “Retriever: Point Cloud Retrieval in Compressed 3D Maps,” in Proc.~of the IEEE Intl.~Conf.~on Robotics & Automation (ICRA), 2022. PDF: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/wiesmann2022icra.pdf #UniBonn #StachnissLab #robotics

Talk by S. Li: Multi-scale Interaction for Real-time LiDAR Data Segmentation … (RAL-ICRA’23)
ICRA’23 Talk about the paper: S. Li, X. Chen, Y. Liu, D. Dai, C. Stachniss, and J. Gall, “Multi-scale Interaction for Real-time LiDAR Data Segmentation on an Embedded Platform,” IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L), vol. 7, iss. 2, pp. 738-745, 2022. doi:10.1109/LRA.2021.3132059 PAPER: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/li2022ral.pdf CODE: https://github.com/sj-li/MINet

Talk by F. Magistri: 3D Shape Completion and Reconstruction for Agricultural Robots (RAL-IROS’22)
IROS 2020 Talk by Federico Magistri on F. Magistri, E. Marks, S. Nagulavancha, I. Vizzo, T. Läbe, J. Behley, M. Halstead, C. McCool, and C. Stachniss, “Contrastive 3D Shape Completion and Reconstruction for Agricultural Robots using RGB-D Frames,” IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L), vol. 7, iss. 4, pp. 10120-10127, 2022. Paper: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/magistri2022ral-iros.pdf
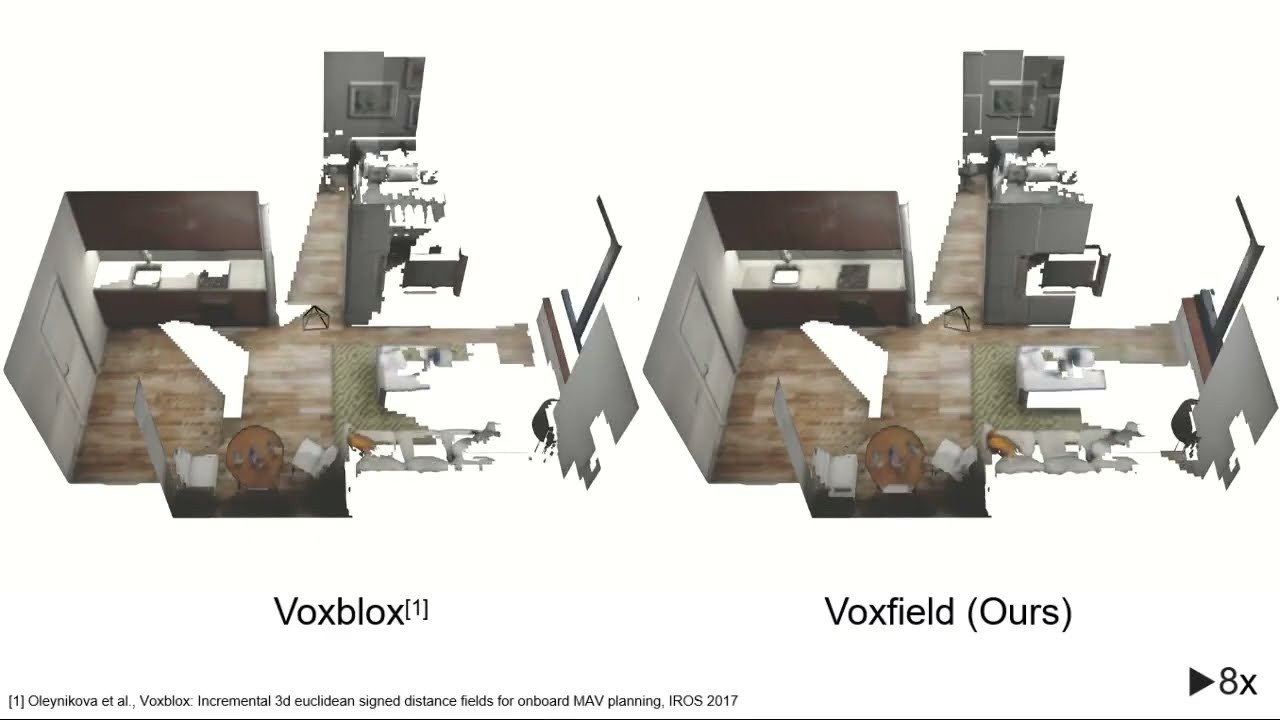
Voxfield: Non-Projective Signed Distance Fieldsfor Online Planning and 3D Reconstruction
Video of the paper “Voxfield: Non-Projective Signed Distance Fieldsfor Online Planning and 3D Reconstruction”, by Matthias Hüppi, Luca Bartolomei, Ruben Mascaro and Margarita Chli, IROS 2022. Abstract – Creating accurate maps of complex, unknown environments is of utmost importance for truly autonomous navigation robot. However, building these maps online is far from trivial, especially when dealing with large amounts of raw sensor readings on a computation and energy constrained mobile system, such as a small drone. While numerous approaches tackling this problem have emerged in recent years, the mapping accuracy is often sacrificed as systematic approximation errors are tolerated for efficiency’s sake. Motivated by these challenges, we propose Voxfield, a mapping framework that can generate maps online with higher accuracy and lower computational burden than the state of the art. Built upon the novel formulation of non-projective truncated signed distance fields (TSDFs), our approach produces more accurate and complete maps, suitable for surface reconstruction. Additionally, it enables efficient generation of Euclidean signed distance fields (ESDFs), useful e.g., for path planning, that does not suffer from typical approximation errors. Through a series of experiments with public datasets, both real-world and synthetic, we demonstrate that our method beats the state of the art in map coverage, accuracy and computational time. Moreover, we show that Voxfield can be utilized as a back-end in recent multi-resolution mapping frameworks, producing high quality maps even in large-scale experiments. Finally, we validate our method by running it onboard a quadrotor, showing it can generate accurate ESDF maps usable for real-time path planning and obstacle avoidance. Paper – https://www.research-collection.ethz.ch/handle/20.500.11850/560719 Code – https://github.com/VIS4ROB-lab/voxfield

IROS 2022- Voxfield: Non-Projective Signed Distance Fields for Online Planning and 3D Reconstruction
Video of the presentation at IROS 2022 of the paper “Voxfield: Non-Projective Signed Distance Fields for Online Planning and 3D Reconstruction” by Yue Pan, Yves Kompis, Luca Bartolomei, Ruben Mascaro, Cyrill Stachniss and Margarita Chli Paper Link – https://www.research-collection.ethz.ch/handle/20.500.11850/560719 Code Link – https://github.com/VIS4ROB-lab/voxfield Abstract – Creating accurate maps of complex, unknown environments is of utmost importance for truly autonomous navigation robot. However, building these maps online is far from trivial, especially when dealing with large amounts of raw sensor readings on a computation and energy constrained mobile system, such as a small drone. While numerous approaches tackling this problem have emerged in recent years, the mapping accuracy is often sacrificed as systematic approximation errors are tolerated for efficiency’s sake. Motivated by these challenges, we propose Voxfield, a mapping framework that can generate maps online with higher accuracy and lower computational burden than the state of the art. Built upon the novel formulation of non-projective truncated signed distance fields (TSDFs), our approach produces more accurate and complete maps, suitable for surface reconstruction. Additionally, it enables efficient generation of Euclidean signed distance fields (ESDFs), useful e.g., for path planning, that does not suffer from typical approximation errors. Through a series of experiments with public datasets, both real-world and synthetic, we demonstrate that our method beats the state of the art in map coverage, accuracy and computational time. Moreover, we show that Voxfield can be utilized as a back-end in recent multi-resolution mapping frameworks, producing high quality maps even in large-scale experiments. Finally, we validate our method by running it onboard a quadrotor, showing it can generate accurate ESDF maps usable for real-time path planning and obstacle avoidance.
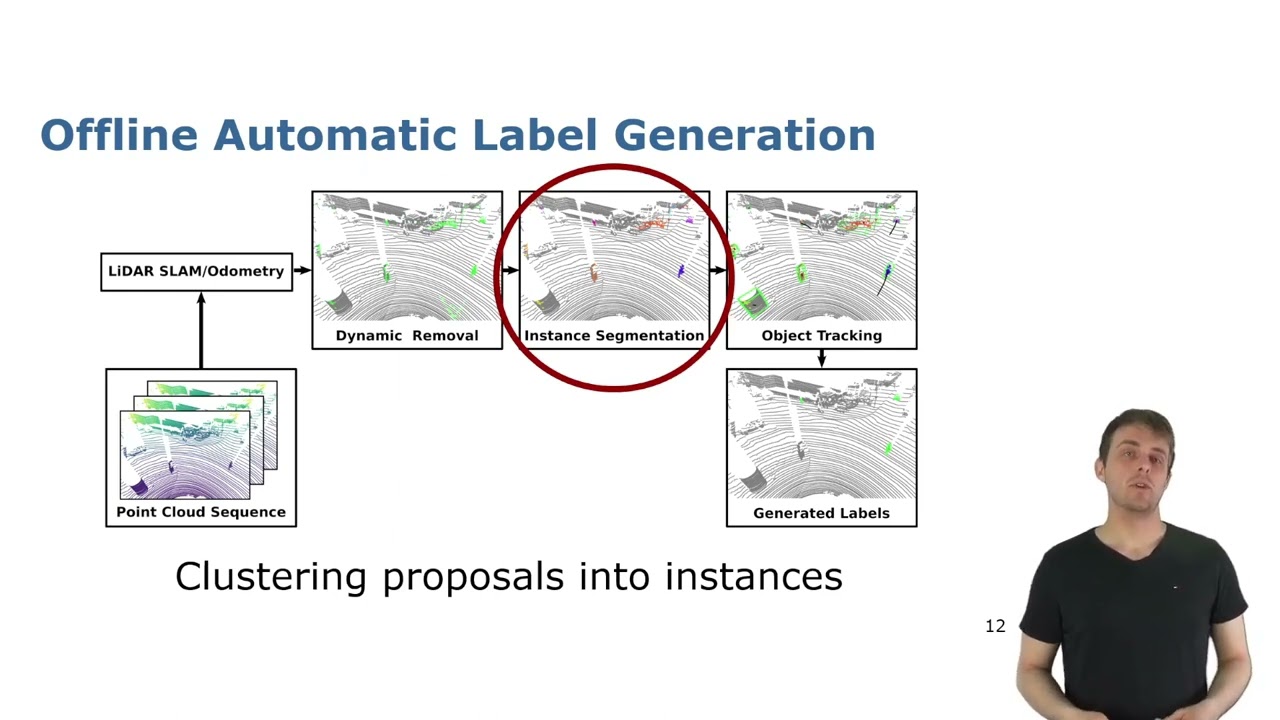
Talk by B. Mersch: Automatic Labeling to Generate Training Data for Online LiDAR MOS (RAL-ICRA’23)
ICRA 2023 Talk for the paper: X. Chen, B. Mersch, L. Nunes, R. Marcuzzi, I. Vizzo, J. Behley, and C. Stachniss, “Automatic Labeling to Generate Training Data for Online LiDAR-Based Moving Object Segmentation,” IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L), vol. 7, iss. 3, pp. 6107-6114, 2022. doi:10.1109/LRA.2022.3166544 PDF: http://arxiv.org/pdf/2201.04501 CODE: https://github.com/PRBonn/auto-mos

Talk by A. Riccardi: Fruit Tracking Over Time Using High-Precision Point Clouds (ICRA’23)
ICRA’23 Talk about the paper: A. Riccardi, S. Kelly, E. Marks, F. Magistri, T. Guadagnino, J. Behley, M. Bennewitz, and C. Stachniss, “Fruit Tracking Over Time Using High-Precision Point Clouds,” in Proc. of the IEEE Intl. Conf. on Robotics & Automation (ICRA), 2023. PDF: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/riccardi2023icra.pdf

Talk by S. Kelly: TAIM – Target-Aware Implicit Mapping for Agricultural Crop Inspection (ICRA’23)
ICRA 2023 Talk by Shane Kelly for the paper: S. Kelly, A. Riccardi, E. Marks, F. Magistri, T. Guadagnino, M. Chli, and C. Stachniss, “Target-Aware Implicit Mapping for Agricultural Crop Inspection,” in Proc. of the IEEE Intl. Conf. on Robotics & Automation (ICRA), 2023.

Talk by I. Vizzo: KISS-ICP: In Defense of Point-to-Point ICP (RAL-IROS’23)
RAL-IROS’23 Talk for the paper: Vizzo, T. Guadagnino, B. Mersch, L. Wiesmann, J. Behley, and C. Stachniss, “KISS-ICP: In Defense of Point-to-Point ICP – Simple, Accurate, and Robust Registration If Done the Right Way,” IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L), vol. 8, iss. 2, pp. 1-8, 2023. doi:10.1109/LRA.2023.3236571 PDF: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/vizzo2023ral.pdf CODE: https://github.com/PRBonn/kiss-icp
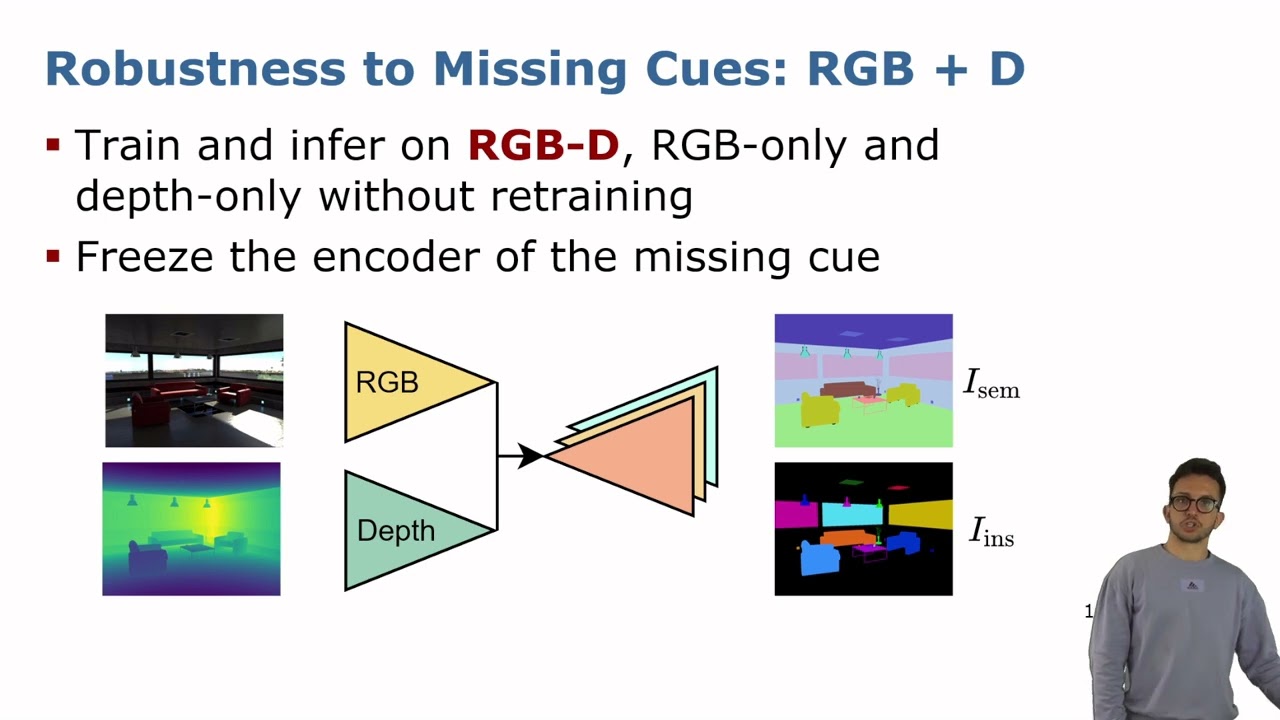
Talk by M. Sodano: Robust Double-Encoder Network for RGB-D Panoptic Segmentation, (ICRA’23)
ICRA’23 Talk about the paper: M. Sodano, F. Magistri, T. Guadagnino, J. Behley, and C. Stachniss, “Robust Double-Encoder Network for RGB-D Panoptic Segmentation,” in Proc. of the IEEE Intl. Conf. on Robotics & Automation (ICRA), 2023. PDF: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/sodano2023icra.pdf CODE: https://github.com/PRBonn/PS-res-excite

Talk by Y. Pan: Panoptic Mapping with Fruit Completion and Pose Estimation … (IROS’23)
IROS’23 Talk for the paper: Y. Pan, F. Magistri, T. Läbe, E. Marks, C. Smitt, C. S. McCool, J. Behley, and C. Stachniss, “Panoptic Mapping with Fruit Completion and Pose Estimation for Horticultural Robots,” in Proc. of the IEEE/RSJ Intl. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2023. PDF: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/pan2023iros.pdf CODE: https://github.com/PRBonn/HortiMapping
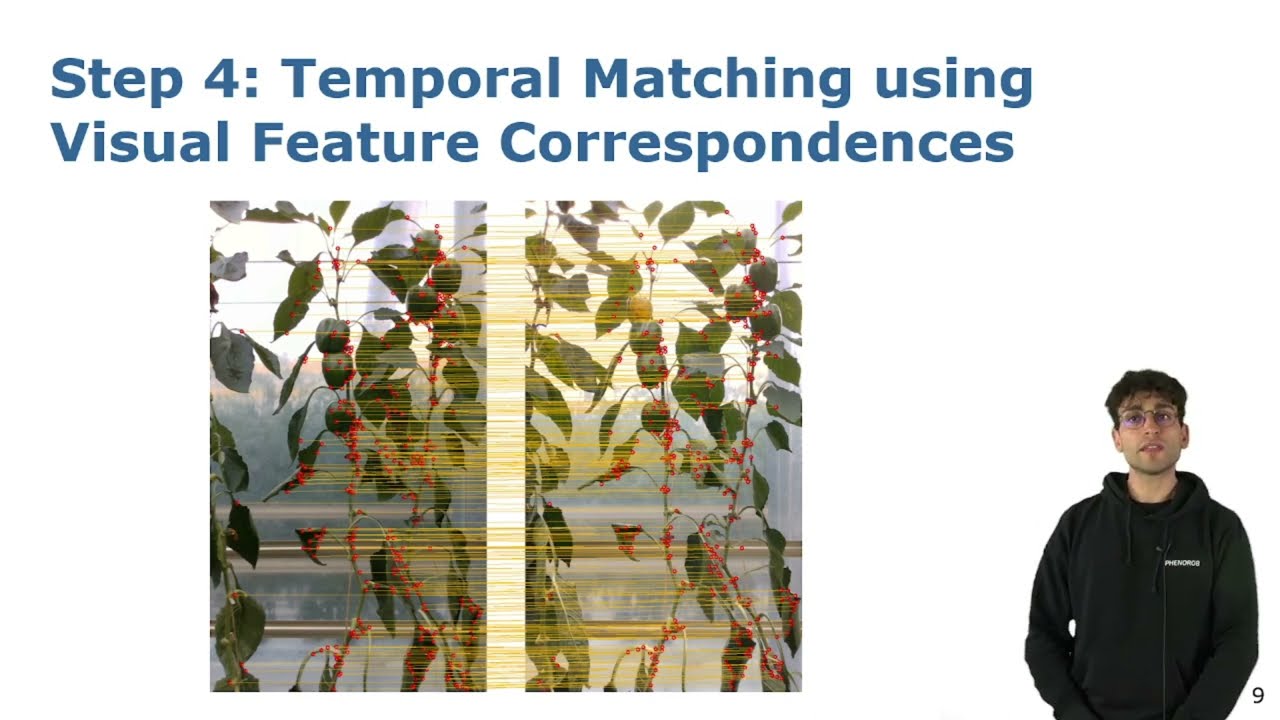
Talk by L. Lobefaro: Estimating 4D Data Associations Towards Spatial-Temporal Mapping … (IROS’23)
IROS’23 Talk for the paper: L. Lobefaro, M. V. R. Malladi, O. Vysotska, T. Guadagnino, and C. Stachniss, “Estimating 4D Data Associations Towards Spatial-Temporal Mapping of Growing Plants for Agricultural Robots,” in Proc. of the IEEE/RSJ Intl. Conf. on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2023. PDF: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/lobefaro2023iros.pdf CODE: https://github.com/PRBonn/plants_temporal_matcher
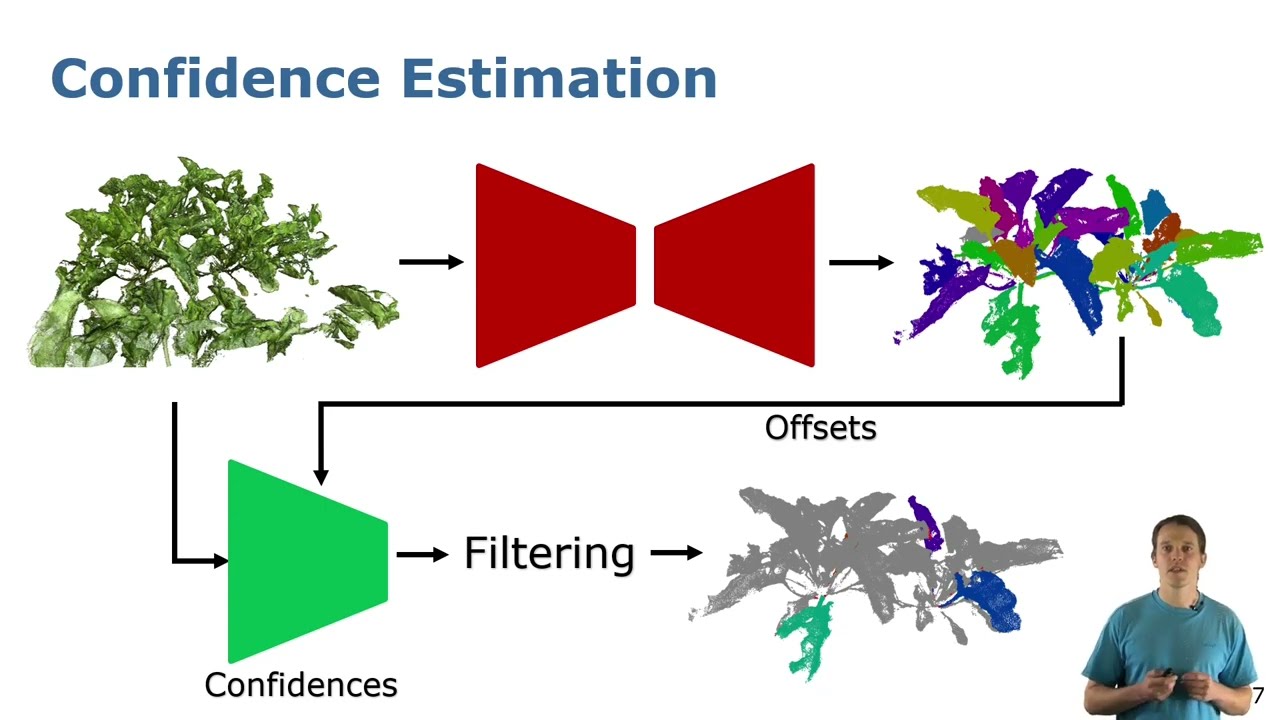
Trailer: High Precision Leaf Instance Segmentation in Point Clouds Obtained Under Real Field…
Trailer for the paper: E. Marks, M. Sodano, F. Magistri, L. Wiesmann, D. Desai, R. Marcuzzi, J. Behley, and C. Stachniss, “High Precision Leaf Instance Segmentation in Point Clouds Obtained Under Real Field Conditions,” IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L), vol. 8, iss. 8, pp. 4791-4798, 2023. doi:10.1109/LRA.2023.3288383 PDF: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/marks2023ral.pdf CODE: https://github.com/PRBonn/plant_pcd_segmenter VIDEO: https://youtu.be/dvA1SvQ4iEY TALK: https://youtu.be/_k3vpYl-UW0
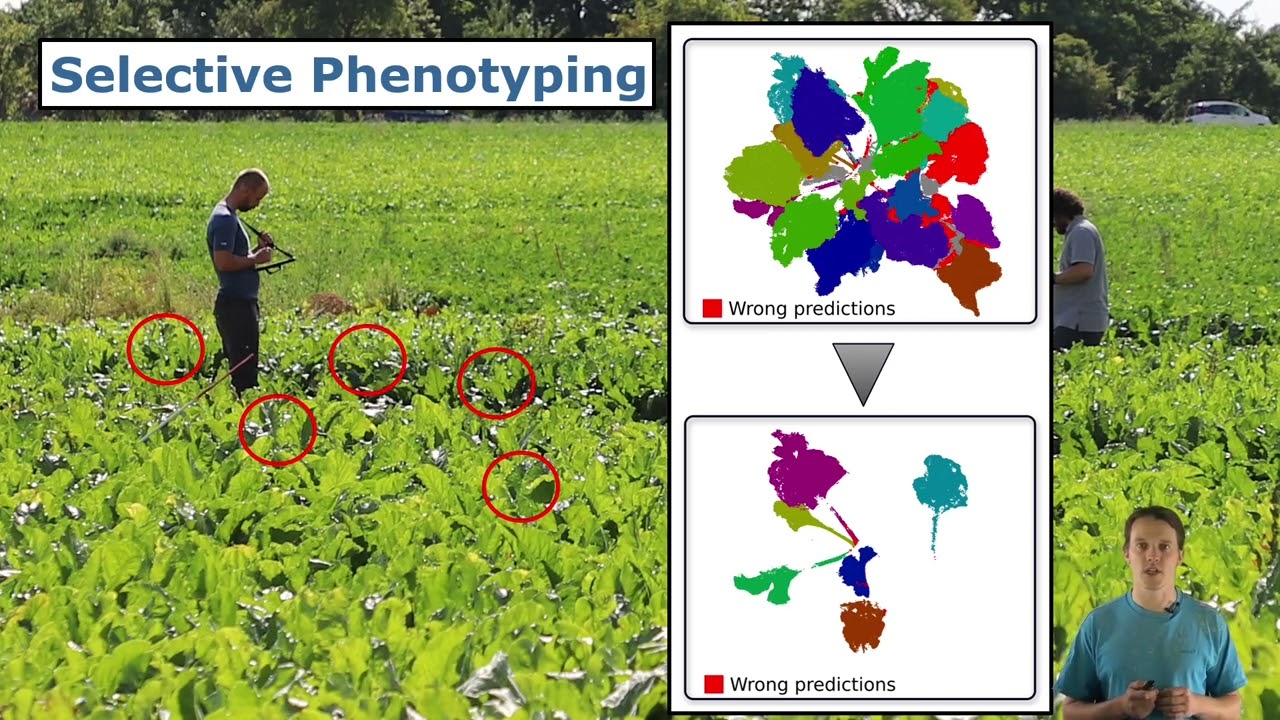
Talk by E. Marks: High Precision Leaf Instance Segmentation in Point Clouds Obtained Under Real…
Talk about the paper: E. Marks, M. Sodano, F. Magistri, L. Wiesmann, D. Desai, R. Marcuzzi, J. Behley, and C. Stachniss, “High Precision Leaf Instance Segmentation in Point Clouds Obtained Under Real Field Conditions,” IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L), vol. 8, iss. 8, pp. 4791-4798, 2023. doi:10.1109/LRA.2023.3288383 PDF: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/marks2023ral.pdf CODE: https://github.com/PRBonn/plant_pcd_segmenter VIDEO: https://youtu.be/dvA1SvQ4iEY TALK: https://youtu.be/_k3vpYl-UW0

NBV-SC: Next Best View Planning based on Shape Completion – IROS23 Paper Presentation
Paper presentation by Rohit Menon given at IROS 2023. For more details, have a glance at the paper! Title: “NBV-SC: Next Best View Planning based on Shape Completion for Fruit Mapping and Reconstruction” Full paper link: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2209.15376.pdf Institute website: https://www.hrl.uni-bonn.de/Members/menon/rohit-menon

Graph-Based View Motion Planning for Fruit Detection – IROS23 Paper Presentation
Paper presentation by Tobias Zaenker given at IROS 2023. For more details, have a glance at the paper! Title: “Graph-Based View Motion Planning for Fruit Detection” Full paper link: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2303.03048.pdf website: https://www.hrl.uni-bonn.de/Members/tzaenker/tobias-zaenker
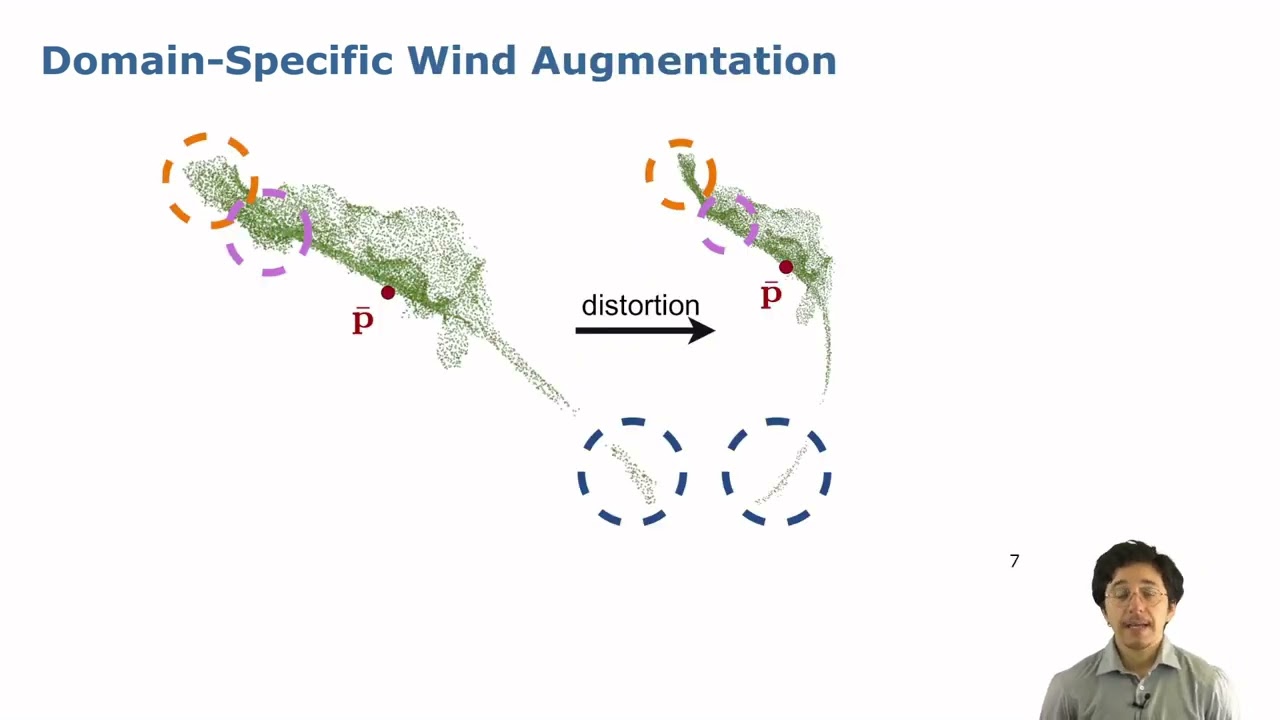
Talk by G. Roggiolani: Unsupervised Pre-Training for 3D Leaf Instance Segmentation (RAL-ICRA’24)
Talk about the paper: G. Roggiolani, F. Magistri, T. Guadagnino, J. Behley, and C. Stachniss, “Unsupervised Pre-Training for 3D Leaf Instance Segmentation,” IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L), vol. 8, pp. 7448-7455, 2023. doi:10.1109/LRA.2023.3320018 PDF: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/roggiolani2023ral.pdf CODE: https://github.com/PRBonn/Unsupervised-Pre-Training-for-3D-Leaf-Instance-Segmentation

Trailer: Unsupervised Pre-Training for 3D Leaf Instance Segmentation (RAL’2023)
Paper trailer about the work: G. Roggiolani, F. Magistri, T. Guadagnino, J. Behley, and C. Stachniss, “Unsupervised Pre-Training for 3D Leaf Instance Segmentation,” IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L), vol. 8, pp. 7448-7455, 2023. doi:10.1109/LRA.2023.3320018 PDF: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/roggiolani2023ral.pdf CODE: https://github.com/PRBonn/Unsupervised-Pre-Training-for-3D-Leaf-Instance-Segmentation

Trailer: Tree Instance Segmentation and Traits Estimation for Forestry Environments… (ICRA’24)
Paper Trailer for the work: M. V. R. Malladi, T. Guadagnino, L. Lobefaro, M. Mattamala, H. Griess, J. Schweier, N. Chebrolu, M. Fallon, J. Behley, and C. Stachniss, “Tree Instance Segmentation and Traits Estimation for Forestry Environments Exploiting LiDAR Data ,” in Proc. of the IEEE Intl. Conf. on Robotics & Automation (ICRA), 2024. PDF: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/malladi2024icra.pdf
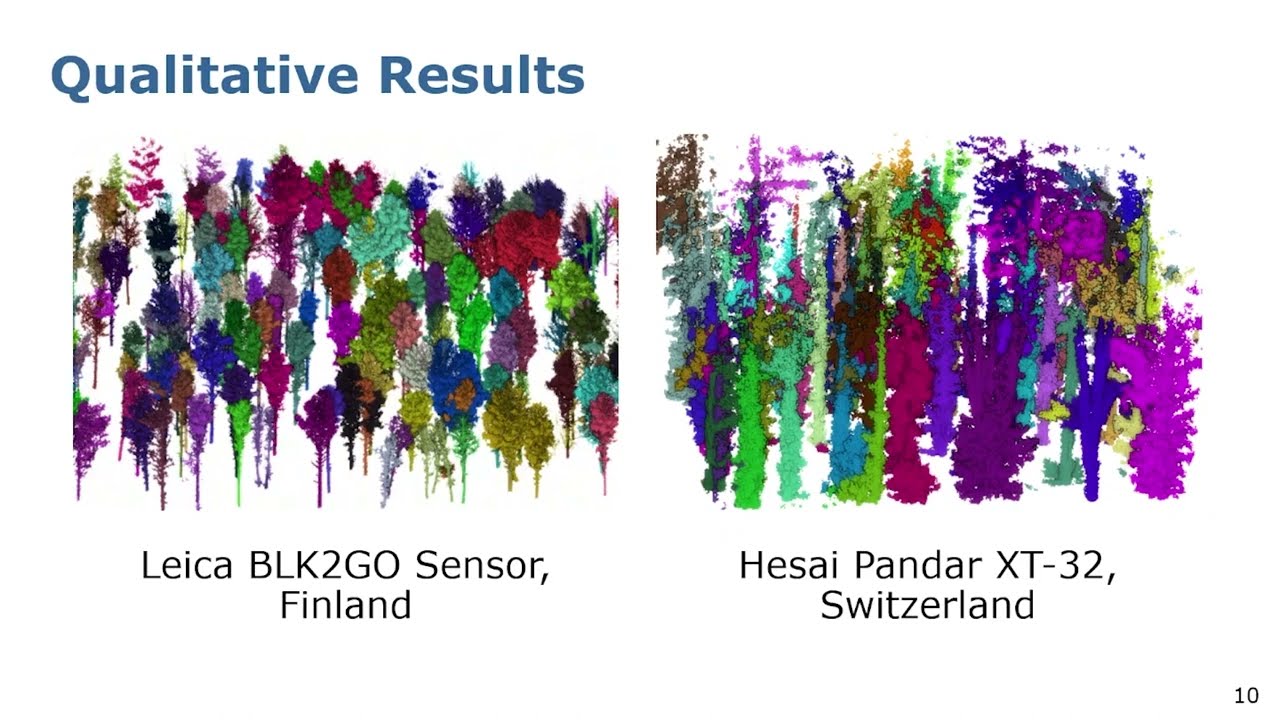
Talk by M. Malladi: Tree Instance Segmentation and Traits Estimation for Forestry Environments…
ICRA’2024 Talk by Meher Malladi about the paper: M. V. R. Malladi, T. Guadagnino, L. Lobefaro, M. Mattamala, H. Griess, J. Schweier, N. Chebrolu, M. Fallon, J. Behley, and C. Stachniss, “Tree Instance Segmentation and Traits Estimation for Forestry Environments Exploiting LiDAR Data ,” in Proc. of the IEEE Intl. Conf. on Robotics & Automation (ICRA), 2024. PDF: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/malladi2024icra.pdf
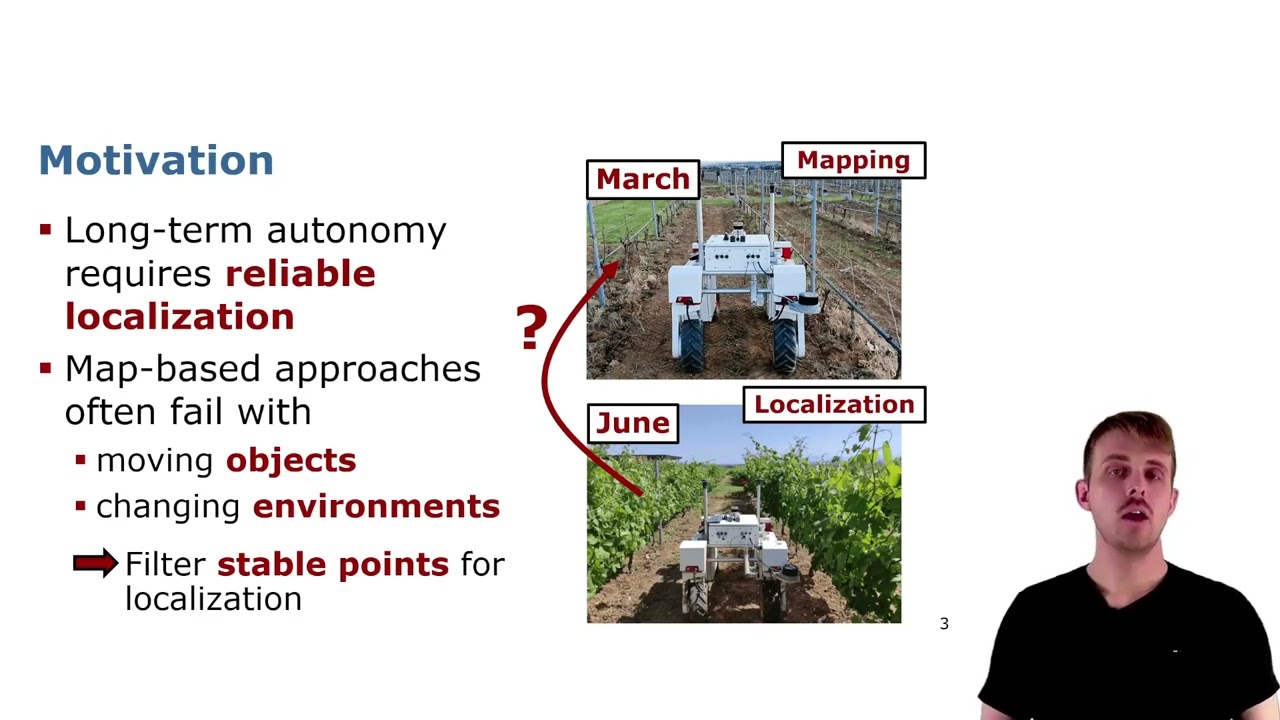
Trailer: Generalizable Stable Points Segmentation for 3D LiDAR Long-Term Localization (RAL’24)
Short Trailer Video for the RAL Paper to be presented at ICRA’2024: I. Hroob, B. Mersch, C. Stachniss, and M. Hanheide, “Generalizable Stable Points Segmentation for 3D LiDAR Scan-to-Map Long-Term Localization,” IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L), vol. 9, iss. 4, pp. 3546-3553, 2024. doi:10.1109/LRA.2024.3368236 PDF: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/hroob2024ral.pdf

Talk by M. Sodano: Open-World Semantic Segmentation Including Class Similarity (CVPR’24)
CVPR 2024 Talk by Matteo Sodano about the paper: M. Sodano, F. Magistri, L. Nunes, J. Behley, and C. Stachniss, “Open-World Semantic Segmentation Including Class Similarity,” in Proc. of the IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2024. PAPER: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/sodano2024cvpr.pdf CODE: https://github.com/PRBonn/ContMAV

Talk by L. Nunes: Scaling Diffusion Models to Real-World 3D LiDAR Scene Completion (CVPR’24)
CVPR 2024 Talk by Lucas Nunes about the paper: L. Nunes, R. Marcuzzi, B. Mersch, J. Behley, and C. Stachniss, “Scaling Diffusion Models to Real-World 3D LiDAR Scene Completion,” in Proc. of the IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2024. PDF: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/nunes2024cvpr.pdf CODE: https://github.com/PRBonn/LiDiff
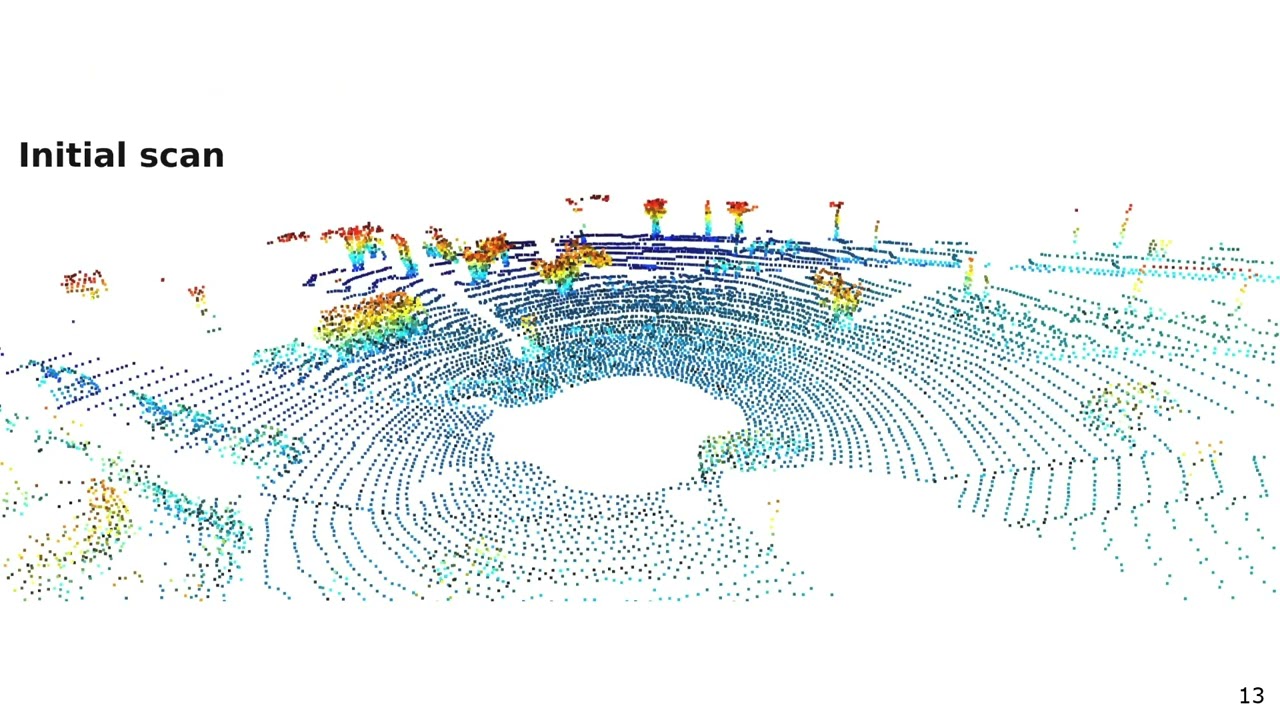
Trailer: Scaling Diffusion Models to Real-World 3D LiDAR Scene Completion (CVPR’24)
Trailer for the paper: L. Nunes, R. Marcuzzi, B. Mersch, J. Behley, and C. Stachniss, “Scaling Diffusion Models to Real-World 3D LiDAR Scene Completion,” in Proc. of the IEEE/CVF Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2024.
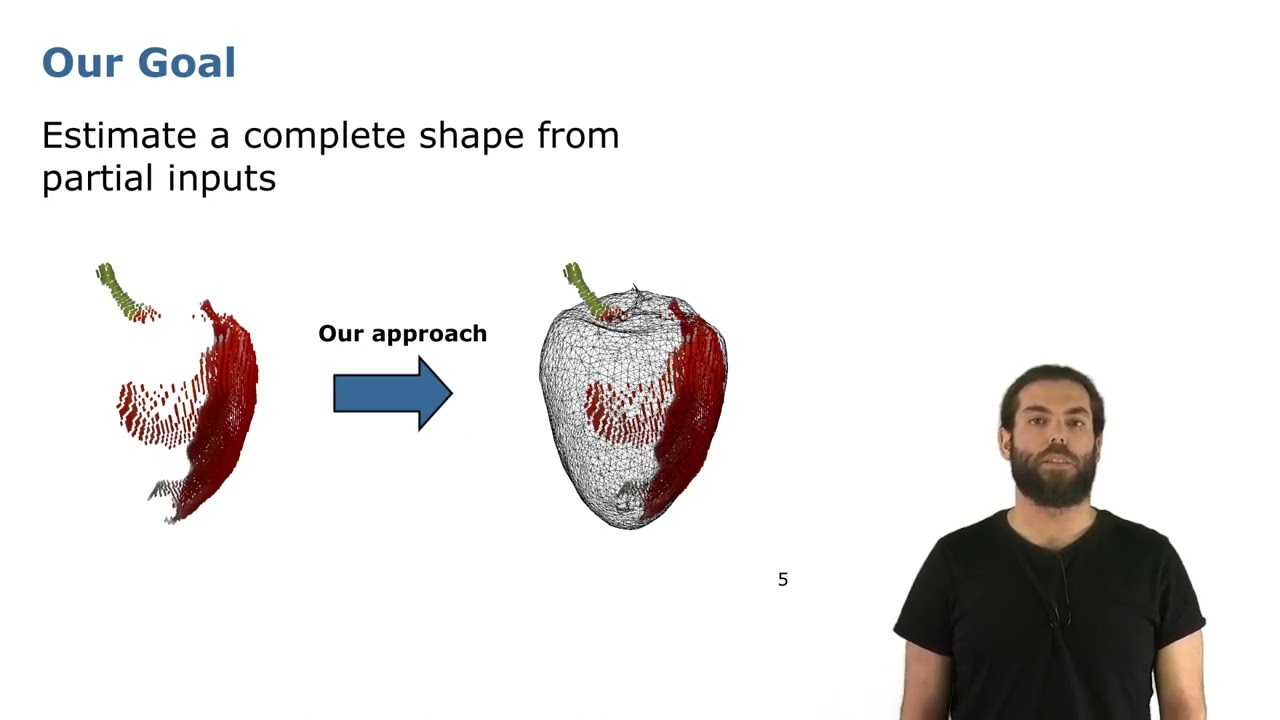
Trailer: Efficient and Accurate Transformer-Based 3D Shape Completion and Reconstruction of Fruits..
Paper Trailer for: F. Magistri, R. Marcuzzi, E. A. Marks, M. Sodano, J. Behley, and C. Stachniss, “Efficient and Accurate Transformer-Based 3D Shape Completion and Reconstruction of Fruits for Agricultural Robots,” in Proc. of the IEEE Intl. Conf. on Robotics & Automation (ICRA), 2024. PDF: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/magistri2024icra.pdf Code (to be released soon): https://github.com/PRBonn/TCoRe

Talk by F. Magistri: Efficient and Accurate Transformer-Based 3D Shape Completion and Reconstruction
ICRA’24 Talk by F. Magistri about the paper: F. Magistri, R. Marcuzzi, E. A. Marks, M. Sodano, J. Behley, and C. Stachniss, “Efficient and Accurate Transformer-Based 3D Shape Completion and Reconstruction of Fruits for Agricultural Robots,” in Proc. of the IEEE Intl. Conf. on Robotics & Automation (ICRA), 2024. Paper Trailer: https://youtu.be/U1xxnUGrVL4 ICRA’24 Talk: https://youtu.be/JKJMEC6zfHE PDF: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/magistri2024icra.pdf Code (to be released soon): https://github.com/PRBonn/TCoRe

Trailer: Effectively Detecting Loop Closures using Point Cloud Density Maps
Paper trailer for the work: S. Gupta, T. Guadagnino, B. Mersch, I. Vizzo, and C. Stachniss, “Effectively Detecting Loop Closures using Point Cloud Density Maps,” in Proc. of the IEEE Intl. Conf. on Robotics & Automation (ICRA), 2024. PDF: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/gupta2024icra.pdf CODE: https://github.com/PRBonn/MapClosures
Talk by S. Gupta: Effectively Detecting Loop Closures using Point Cloud Density Maps (ICRA’2024)
Talk at ICRA’2024 about the paper: S. Gupta, T. Guadagnino, B. Mersch, I. Vizzo, and C. Stachniss, “Effectively Detecting Loop Closures using Point Cloud Density Maps,” in Proc. of the IEEE Intl. Conf. on Robotics & Automation (ICRA), 2024. PDF: https://www.ipb.uni-bonn.de/wp-content/papercite-data/pdf/gupta2024icra.pdf CODE: https://github.com/PRBonn/MapClosures

Active Implicit Reconstruction using One-Shot View Planning
This video demonstrates the work presented in our paper “Active Implicit Reconstruction using One-Shot View Planning” by H. Hu*, S. Pan*, L. Jin, M. Popović, and M. Bennewitz, submitted to ICRA 2024 (*equal contribution). Paper link: TBD Active object reconstruction using autonomous robots is gaining great interest. A primary goal in this task is to maximize the information of the object to be reconstructed, given limited on-board resources. Previous view planning methods exhibit inefficiency since they rely on an iterative paradigm based on explicit representations, consisting of (1) planning a path to the next-best view only; and (2) requiring a considerable number of less-gain views in terms of surface coverage. To address these limitations, in this video, we integrated implicit representations into the One-Shot View Planning (OSVP) that directly predict a set of views. The key idea behind our approach is to use implicit representations to obtain the small missing surface areas instead of observing them with extra views. The real-world comparative experiments in this video support the claim that our method achieves sufficient reconstruction quality within less movement costs under the same view budget compared to explicit NBV method. code: github.com/psc0628/AIR-OSVP
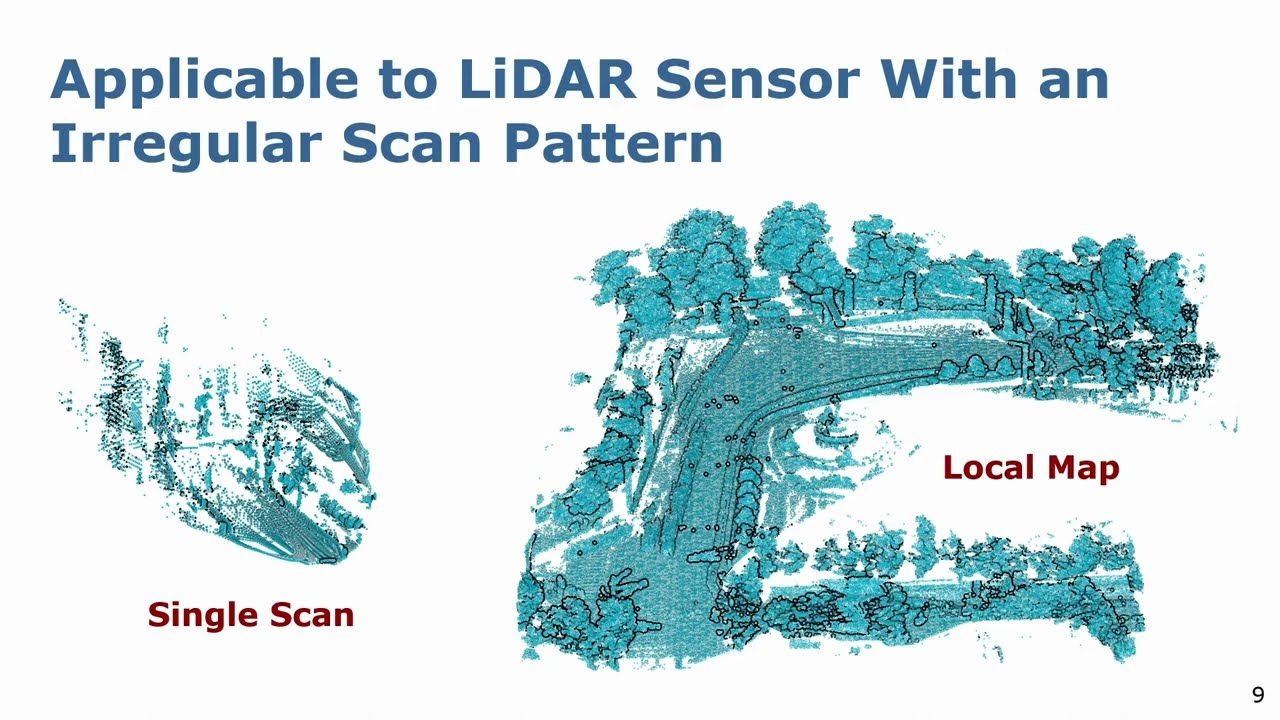
ICCV’19: SemanticKITTI: A Dataset for Semantic Scene Understanding of LiDAR Sequences, Behley et al.
With SemanticKITTI, we release a large dataset to propel research on laser-based semantic segmentation. We annotated all sequences of the KITTI Vision Odometry Benchmark and provide dense point-wise annotations for the complete 360 deg field-of-view of the employed automotive LiDAR. We propose three benchmark tasks based on this dataset: (i) semantic segmentation of point clouds using a single scan, (ii) semantic segmentation using sequences comprised of multiple past scans, and (iii) semantic scene completion, which requires to anticipate the semantic scene in the future. We provide baseline experiments and show that there is a need for more sophisticated models to efficiently tackle these tasks. See: http://semantic-kitti.org J. Behley, M. Garbade, A. Milioto, J. Quenzel, S. Behnke, C. Stachniss, and J. Gall, “SemanticKITTI: A Dataset for Semantic Scene Understanding of LiDAR Sequences,” in Proc. of the IEEE/CVF International Conf.~on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2019. PDF: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1904.01416.pdf

Jan Weyler – Joint Plant Instance Detection and Leaf Count Estimation for In-Field Plant Phenotyping
International Conference on Digital Technologies for Sustainable Crop Production (DIGICROP 2020) • November 1-10, 2020 • http://digicrop.de/
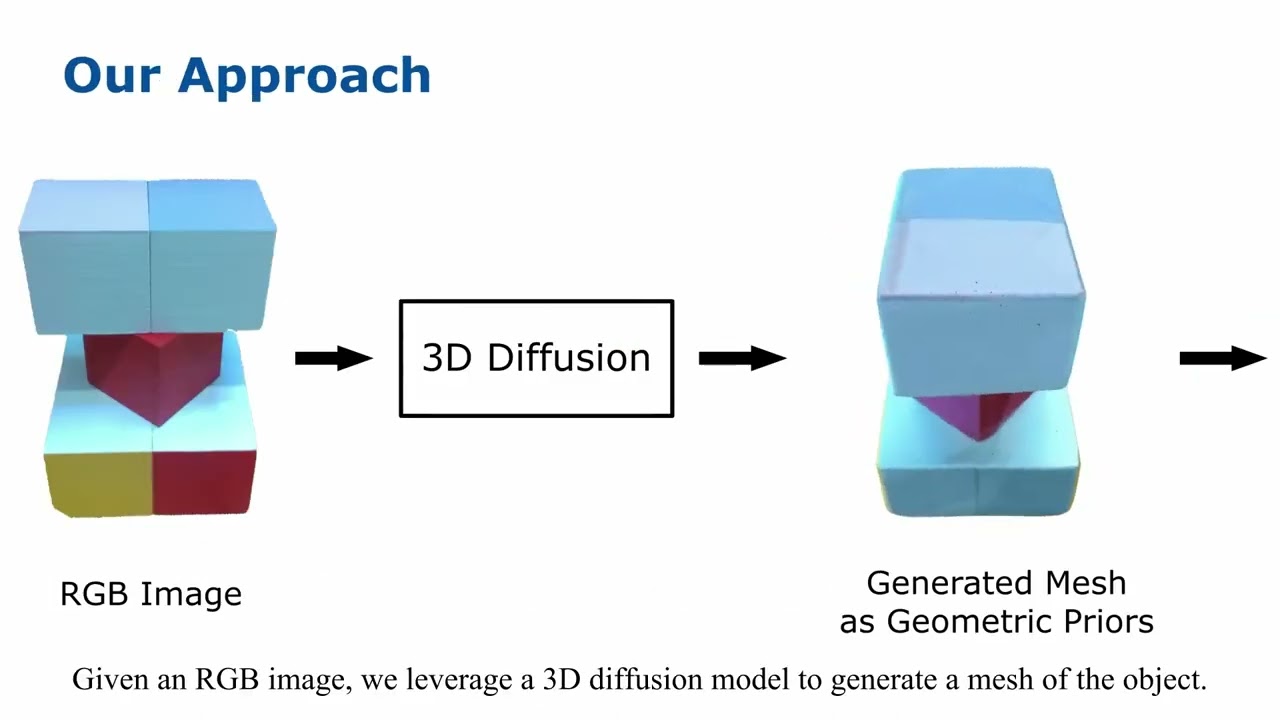
Exploiting Priors from 3D Diffusion Models for RGB-Based One-Shot View Planning
This video demonstrates the work presented in our paper “Exploiting Priors from 3D Diffusion Models for RGB-Based One-Shot View Planning” by S. Pan*, L. Jin*, X. Huang, C. Stachniss, M. Popović, and M. Bennewitz, submitted to IROS 2024 (*equal contribution). Paper link: To reconstruct an initially unknown object, one-shot view planning enables efficient data collection by predicting view configurations and planning the globally shortest path connecting all views at once. However, geometric priors about the object are required to conduct one-shot view planning. In this video, we propose a novel one-shot view planning approach that utilizes the powerful 3D generation capabilities of diffusion models as priors. By incorporating such geometric priors into our pipeline, we achieve effective one-shot view planning starting with only a single RGB image of the object to be reconstructed. The real-world experiments in this video support the claim that our approach balances well between object reconstruction quality and movement cost. code: github.com/psc0628/DM-OSVP

How Many Views Are Needed to Reconstruct an Unknown Object Using NeRF?
This video demonstrates the work presented in our paper “How Many Views Are Needed to Reconstruct an Unknown Object Using NeRF?” by S. Pan*, L. Jin*, H. Hu, M. Popović, and M. Bennewitz, submitted to ICRA 2024 (*equal contribution). Paper link: TBD Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) are gaining significant interest for online active object reconstruction due to their exceptional memory efficiency and requirement for only posed RGB inputs. Previous NeRF-based view planning methods exhibit computational inefficiency since they rely on an iterative paradigm, consisting of (1) retraining the NeRF when new images arrive; and (2) planning a path to the next best view only. To address these limitations, in this video, we propose a non-iterative pipeline based on the Prediction of the Required number of Views (PRV). The key idea behind our approach is that the required number of views to reconstruct an object depends on its complexity. The real-world experiments in this video support the claim that our method predicts a suitable required number of views and achieve sufficient NeRF reconstruction quality with a short global path. code: github.com/psc0628/NeRF-PRV

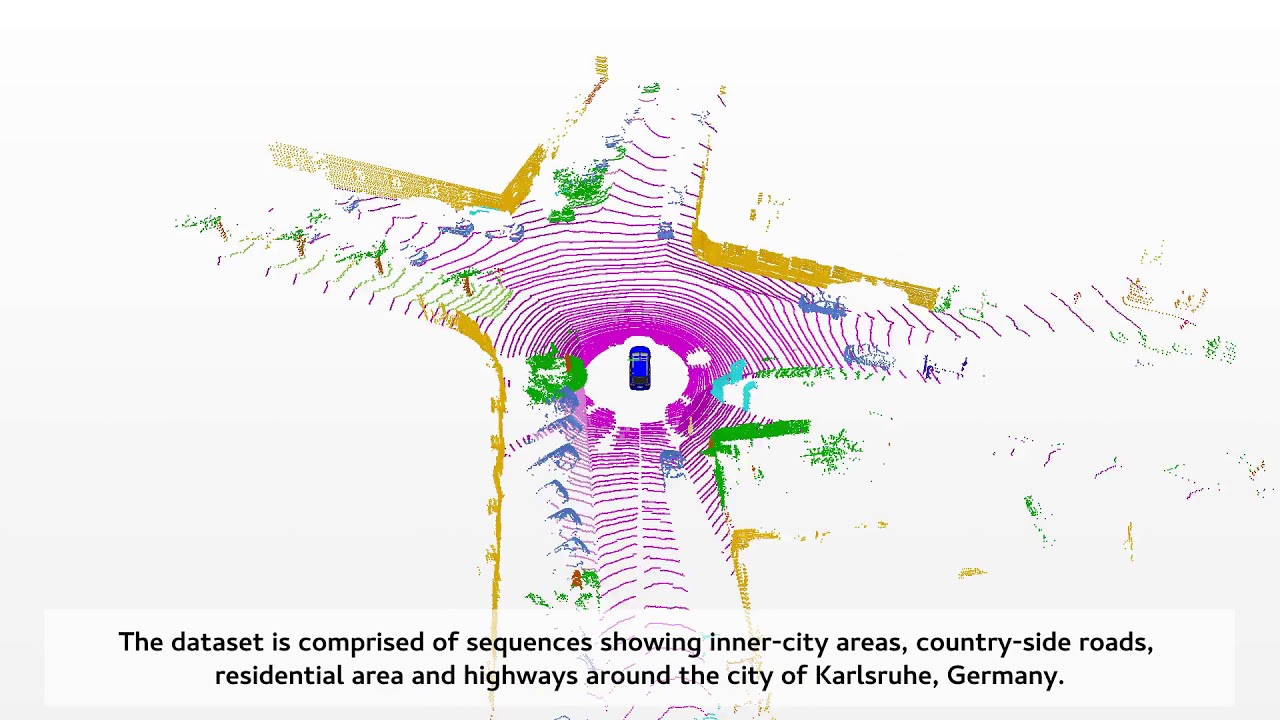
RangeNet++: Fast and Accurate LiDAR Semantic Segmentation
IROS’2019 submission – Andres Milioto, Ignacio Vizzo, Jens Behley, Cyrill Stachniss. Predictions from Sequence 13 Kitti dataset. Each frame is processed individually, and in under 100ms in a single GPU, under the frame rate of a Velodyne LiDAR scanner. Code and data coming soon. Resources: CODE Slam [SuMa]: https://github.com/jbehley/SuMa CODE Semantics [Lidar-Bonnetal]: https://github.com/PRBonn/lidar-bonnetal Kitti dataset: http://www.cvlibs.net/datasets/kitti/ Semantic dataset: http://semantic-kitti.org We thank NVIDIA Corporation for providing a Quadro P6000 GPU used to support this research.
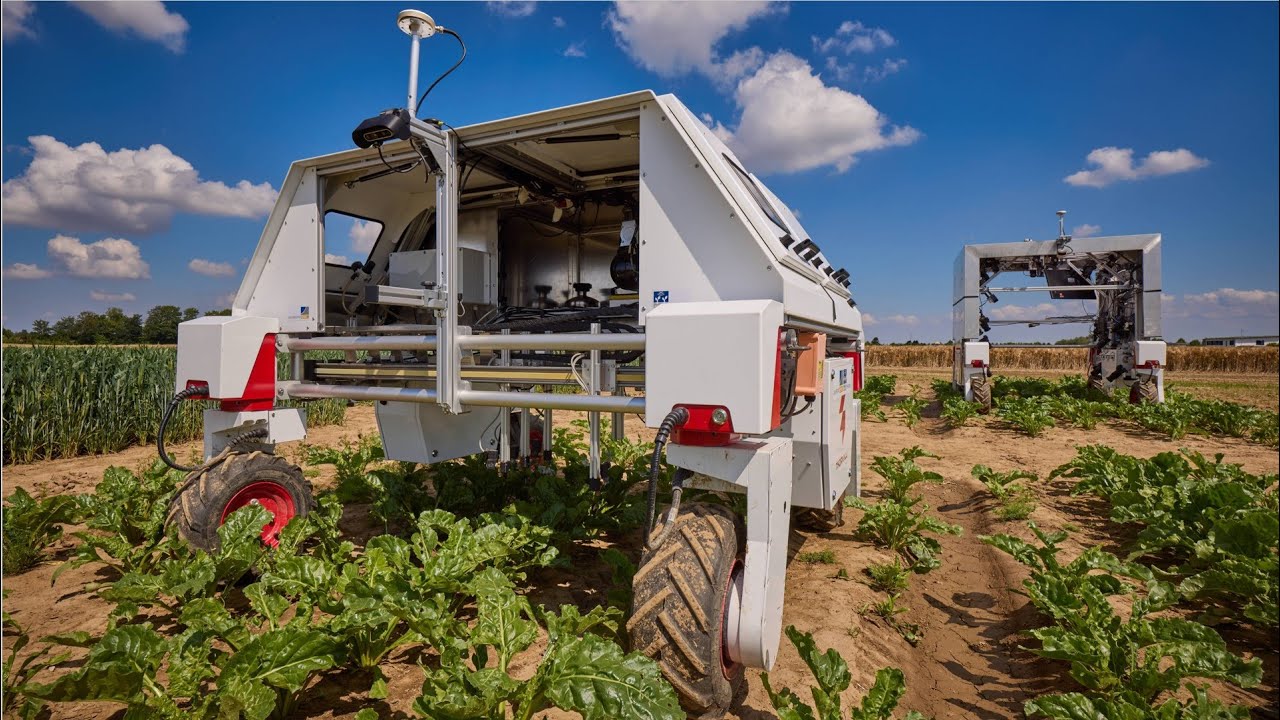

PhenoRob: Research Priorities to Leverage Smart Digital Technologies for Sustainable Crop Production
Agriculture today faces significant challenges that require new ways of thinking, such as smart digital technologies that enable innovative approaches. However, research gaps limit their potential to improve agriculture. In our PhenoRob paper “Research Priorities to Leverage Smart Digital Technologies for Sustainable Crop Production”, Sabine Seidel, Hugo Storm and Lasse Klingbeil outline an interdisciplinary agenda to address the key research gaps and advance sustainability in agriculture. They identify four critical areas: 1. Monitoring to detect weeds and the status of surrounding crops 2. Modelling to predict the yield impact and ecological impacts 3. Decision making by weighing the yield loss against the ecological impact 4. Model uptake, for example policy support to compensate farmers for ecological benefits Closing these gaps requires strong interdisciplinary collaboration. In PhenoRob, this is achieved through five core experiments, seminar and lecture series, and interdisciplinary undergraduate and graduate teaching activities. The paper is available at: H. Storm, S. J. Seidel, L. Klingbeil, F. Ewert, H. Vereecken, W. Amelung, S. Behnke, M. Bennewitz, J. Börner, T. Döring, J. Gall, A. -K. Mahlein, C. McCool, U. Rascher, S. Wrobel, A. Schnepf, C. Stachniss, and H. Kuhlmann, “Research Priorities to Leverage Smart Digital Technologies for Sustainable Crop Production,” European Journal of Agronomy, vol. 156, p. 127178, 2024. doi:10.1016/j.eja.2024.127178 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1161030124000996?via%3Dihub